Fig. 1.
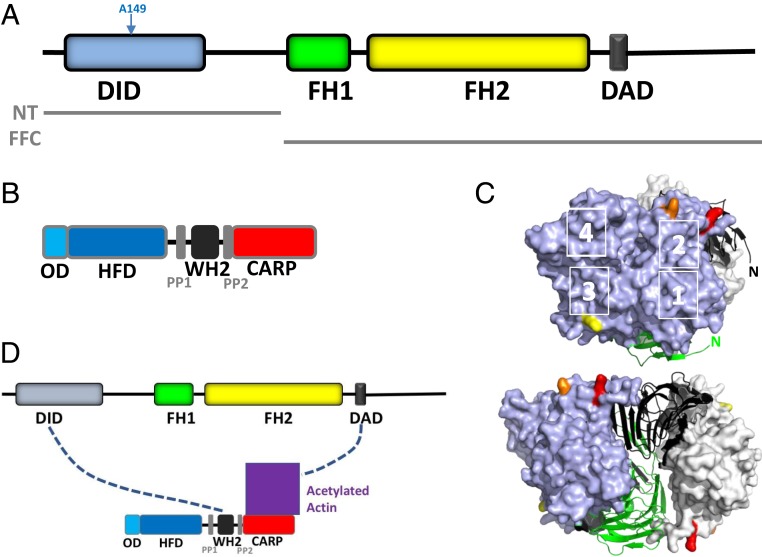
INF2, CAP, and the bridge model of INF2 inhibition. (A) Schematic of human INF2-nonCAAX (1,240 amino acids), including DID (amino acids 32 to 261), formin homology 1 domain (FH1; amino acids 421 to 520), formin homology 2 domain (FH2; amino acids 554 to 940), and DAD/WH2 (amino acids 971 to 1,000). Boundaries of the N-terminal construct (NT) and FH1-FH2-C (FFC) construct used in this study are also shown. (B) Schematic of human CAP2 (477 amino acids), including oligomerization domain (OD; amino acids 1 to 42), HFD (amino acids 43 to 217), proline-rich region 1 (PP1; amino acids 229 to 245), WH2 motif (amino acids 254 to 297), proline-rich region 2 (PP2; amino acids 308 to 323), and CARP domain (amino acids 324 to 477). (C) Actin monomers (blue, gray surfaces) bound to the dimeric CARP domain of CAP1 (black, green ribbons). K50, K61, and K328 on actin are highlighted in red, orange, and yellow, respectively. Actin subdomains are indicated by white numbers. N, amino-termini of CARP subunits. Adapted from Protein Data Bank ID code 6FM2, data from ref. 12. (Bottom) Structure rotated 90° to the left. (D) Bridge model of INF2 inhibition by CAP/actin, whereby INF2-DID interacts with CAP-WH2 while INF2-DAD interacts with acetylated actin, which is bound to the CARP domain of CAP.