Fig. 1.
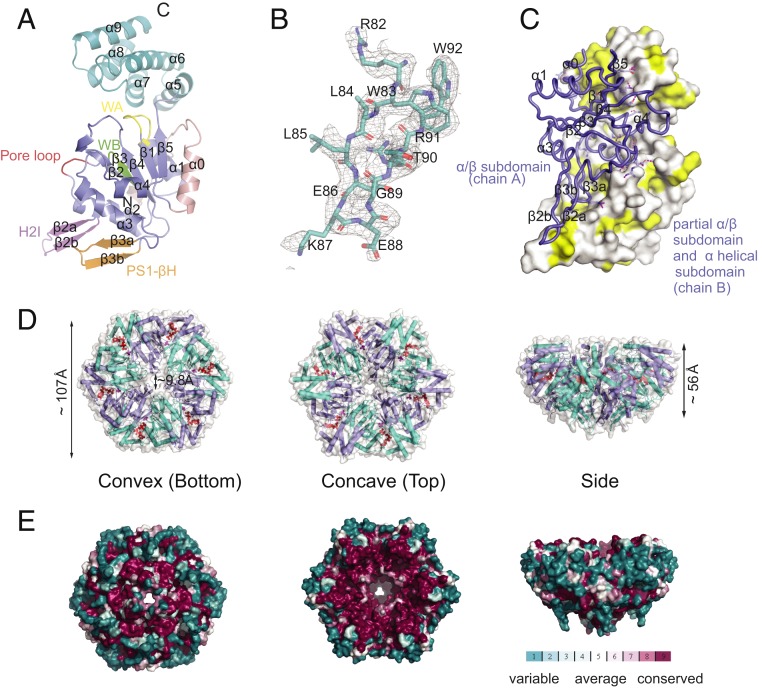
The crystal structure of AfCbbQ2 (A) Schematic representation of an AfCbbQ2 monomer. H2I, helix 2 insert; PS1-βH, presensor 1-β hairpin; WA, Walker A motif; WB, Walker B motif. (B) The Fo-Fc map of the AfCbbQ2 H2I. Residues are shown as sticks, with O, N, and C atom colored red, blue, and deep teal, respectively. (C) View of the dimer interface between the α/β subdomain of one subunit (chain A) and the α-helical subdomain and α/β subdomain of the adjacent subunit (chain B). The α/β and the α-helical subdomains of chain B are shown in surface, and the α/β subdomain of chain A is shown as ribbon. Hydrophobic side chains on the α/β subdomain of chain B are shown in yellow. (D) Surface representation of the AfCbbQ2 hexamer formed by chain A (colored slate) and chain B (colored cyan) dimer and its adjacent 2 dimers by expanding crystallographic symmetry of chain A and chain B. ADP and Pi of each subunit are shown as red spheres. (E) A sequence alignment of 100 CbbQ2 sequences was used to map surface conservation onto the AfCbbQ2 hexamer.