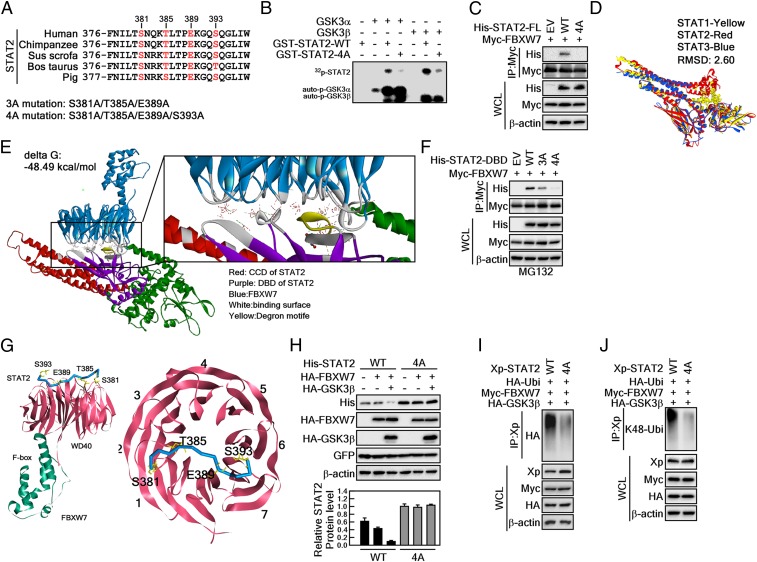
Fig. 5.
GSK3β-mediated STAT2 phosphorylation at degron motifs plays a key role in FBXW7-mediated STAT2 protein stability. (A) Amino acid alignment of the putative degron motifs in the DNA binding domain of STAT2. (B) In vitro kinase assay using GSK3α and -β with STAT2-WT and STAT2-4A. The 4-point mutant (STAT2-4A) of STAT2 at S381A/T385A/E389A/S393A inhibited GSK3α/β-mediated STAT2 phosphorylation. The 32P-labeling of STAT2 was visualized by autoradiography. (C) The 4-point mutant of full-length STAT2 at S381A/T385A/E389A/S393A (STAT2-FL-4A) abolished interaction with FBXW7. (D) Superimposed structures of STAT1, STAT2, and STAT3. Yellow, STAT1; red, STAT2; blue, STAT3. (E) Protein–protein docking of STAT2 and FBXW7. The z-rank score implies the binding energy (kcal/mol). Red, CCD of STAT2; purple, DBD of STAT2; blue, FBXW7; gray, binding surface between STAT2 and FBXW7; yellow, degron motifs. FBXW7 X-ray crystal structure (PDB ID code 2OVP). The interacting amino acids between STAT2 and FBXW7 are provided in the SI Appendix, Fig. S2. (F) WB analysis of WCLs derived from 293T cells transfected with Myc-FBXW7 and His-STAT2-DBD-WT, His-STAT2-DBD-3A, or His-STAT2-DBD-4A. (G, Left) Interaction surface of STAT2 degron motifs containing pS381/pT385/E389/pS393 and WD40 domains of FBXW7. (Right) STAT2 bound across the narrow face of the FBXW7 β-propeller structure. (H) Comparison of the binding between 3- and 4-point mutants of STAT2-DBD on the FBXW7. STAT2-DBD-4A indicates the mutation at S381A/T385A/E389A/S393A. (I and J) WB analysis of WCLs and IPs derived from 293T cells transfected with Xp-STAT2-WT, Xp-STAT2-4A, Myc-FBXW7, or HA-GSK3β. The cells were treated with 10 μM MG132 for 4 h before harvesting.