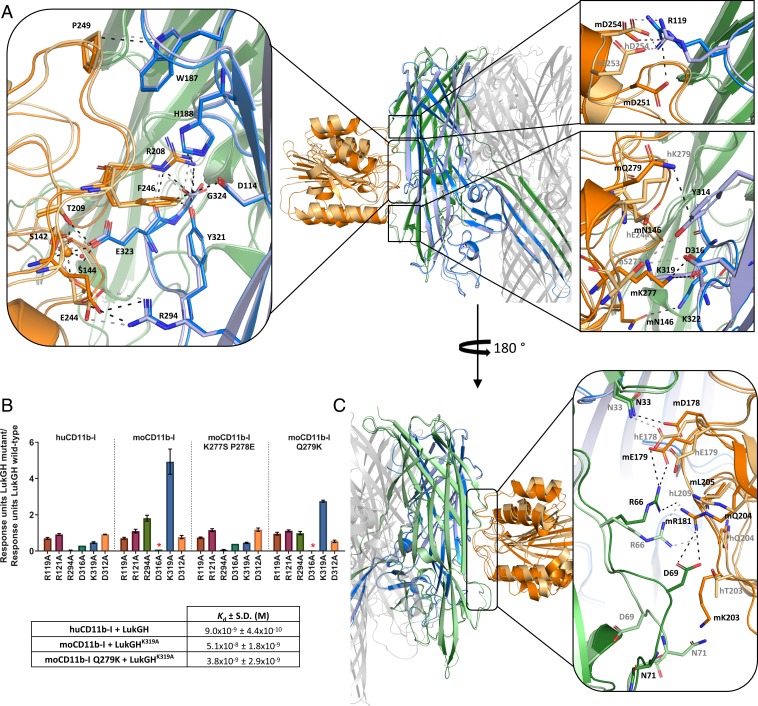
Fig. 2.
Binding epitope of LukGH-CD11b-I. (A) Binding epitopes of LukH–CD11b-I with detailed views of the specific interactions involved in CD11b-I binding in boxes, aligned on LukH. LukG, LukH, and CD11b-I from the LukGHK319A–moCD11b-I structure are shown in green, blue, and orange, respectively. The same protein components from the LukGH–huCD11b-I structure are shown in pale green, pale blue, and pale orange. Hydrogen bonds, salt bridges, the coordinate covalent bonds of Mg2+, as well as some other selected close contacts are shown as dashed lines colored black (for the moCD11b-I complex) or gray (for the huCD11b-I complex). (Left) Conserved interactions; (Right Upper and Lower) nonconserved interactions between the human and the mouse complexes. (B) Binding of LukGH mutants to CD11b-I variants relative to LukGH wild-type (mean of 3 independent experiments ±SEM, except for LukGHD316A with one experiment). Asterisks represent samples where no binding was detected (RU < 0.05 nm). Inset table shows Kd of selected LukGH and CD11b-I variants (mean of 2 to 3 independent experiments ±SD). (C) Binding epitopes of LukG-CD11b-I with a detailed view of the specific interactions involved in CD11b-I binding in the box, aligned on LukH. Color coding as in A.