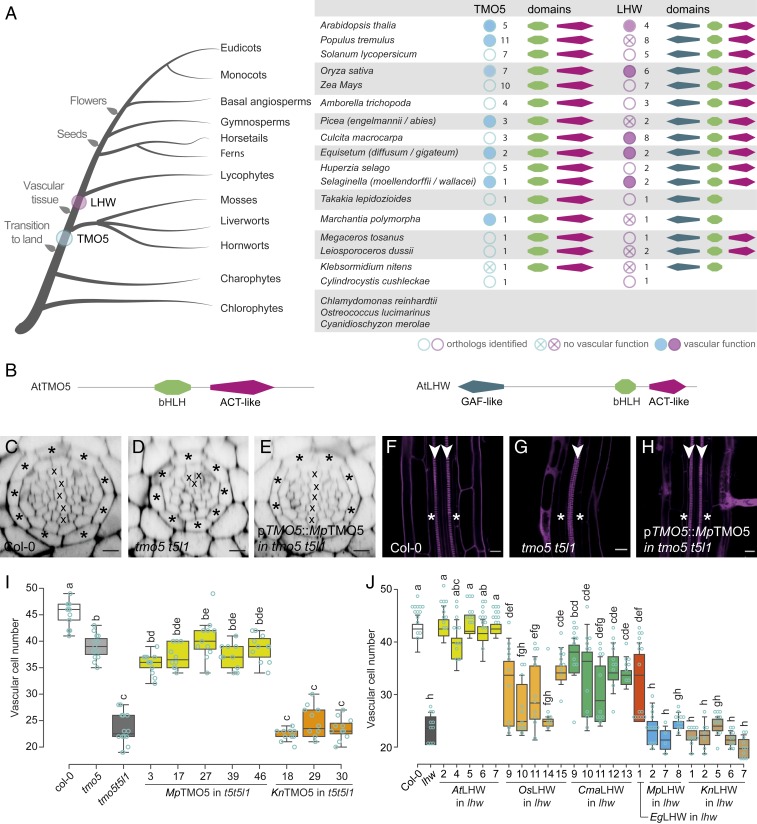
Fig. 2.
Acquisition of PRD function by extant TMO5 and LHW proteins. (A) Summary of TMO5 and LHW orthologs in representative species throughout the plant kingdom. Orthologs tested in complementation assays are marked by a blue or purple solid circle if complementation was observed and by a crossed circle if there was no complementation. The associated number of orthologs retrieved and the presence of specific protein domains (as mentioned in B) are indicated as well. (B) Protein domain architecture of AtTMO5 and AtLHW. (C–J) Interspecies complementation analysis of TMO5 (C–I) and LHW (J) orthologs. (C–H) Representative cross-section (C–E) and longitudinal sections (F–H) of a wild-type (C and F; Col-0), tmo5 t5l1 mutant (D and G), and a line carrying the pTMO5::MpTMO5 transgene in the tmo5 t5l1 background (E and H). Cell-file numbers in the vascular tissue (encircled by the endodermis layer; asterisks) were quantified in cross-sections and represented in box plots for TMO5 (I) and LHW (J) orthologs. Lowercase letters in I and J indicate significantly different groups as determined using a one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey HSD testing. Blue open circles in I and J represent data points. The presence of a diarch vascular architecture was used as another sign of complementation. Crosses in C–E mark xylem cell files; arrowheads (F–H) indicate xylem poles. (Scale bars in C–H, 20 µm.)