Fig. 2.
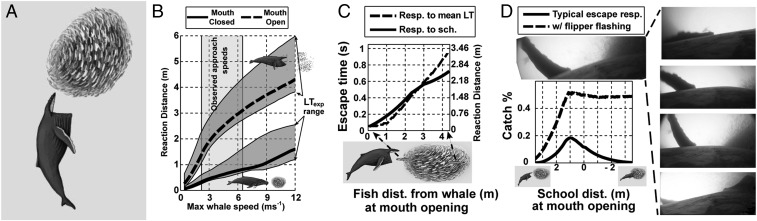
Anchovies are evolutionarily conditioned to avoid small, fast, and mobile particulate feeding predators by forming and reacting as dense schools. Humpback whales, as less commonly encountered predators, take advantage of this strategy in 4 ways: (A) Lunge filter feeding enables engulfment of many individuals simultaneously. (B) MO close to the school results in shorter prey reaction distances equivalent to the whale’s distance at apparent MO (AMO). This value will be intermediate between the 2 extremes of theoretical approaches (mouth always open and mouth always closed). (C) Anchovies at the back of a fleeing school will respond directly to the fish fleeing around it, however, these fish have less time to respond (resulting in a shorter reaction distance) than if they could see the approaching predator directly. (D) Humpback whale flippers can be 3 to 4 m in length—although not themselves used as weapons, they have white undersides that can be used to scare escaping fish back toward the school (see also Fig. 4 and Movie S4).