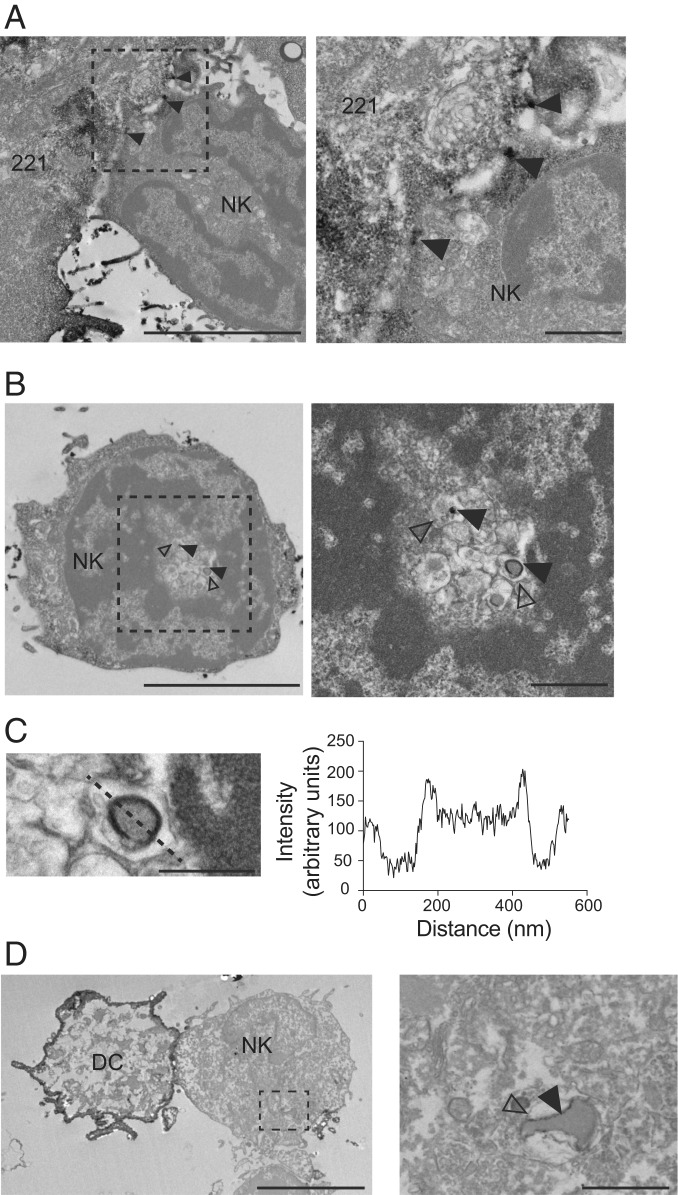
Fig. 3.
Detection of IL-15Rα in NK cells on TEM. 221–Venus-IL-15Rα cells were preloaded with IL-15 (5 nM) and conjugated with primary human NK cells for 30 min. Cells were fixed and stained with a polyclonal antibody to GFP and a secondary antibody coupled to peroxidase. IL-15Rα was detected by the presence of an insoluble black precipitate. (A) IL-15Rα at the 221–NK cell synapse (arrowheads). (Right) Zoom-in view. (Scale bars: 5 μm and 1 μm.) (B) IL-15Rα detected inside an NK cell (filled arrowheads). Open arrowheads point to the membrane of the compartment surrounding the IL-15Rα+ vesicle. (Right) Zoom-in view. (Scale bars: 5 μm and 1 μm.) (C) Detail of the IL-15Rα+ vesicle shown in B. The intensity of signal scanned across the vesicle (dotted line) is shown on the right. (Scale bar: 500 nm.) (D) Primary DCs expressing Venus-IL-15Rα and preloaded with IL-15 (5 nM) were conjugated with primary autologous human NK cells for 30 min. Cells were fixed and stained as described above. IL-15Rα is detected on a vesicle internalized by the NK cell (filled arrowhead). The open arrowhead indicates the membrane of the vesicle containing the IL-15Rα+ vesicle. (Right) Zoom-in view. (Scale bars: 5 μm and 1 μm.)