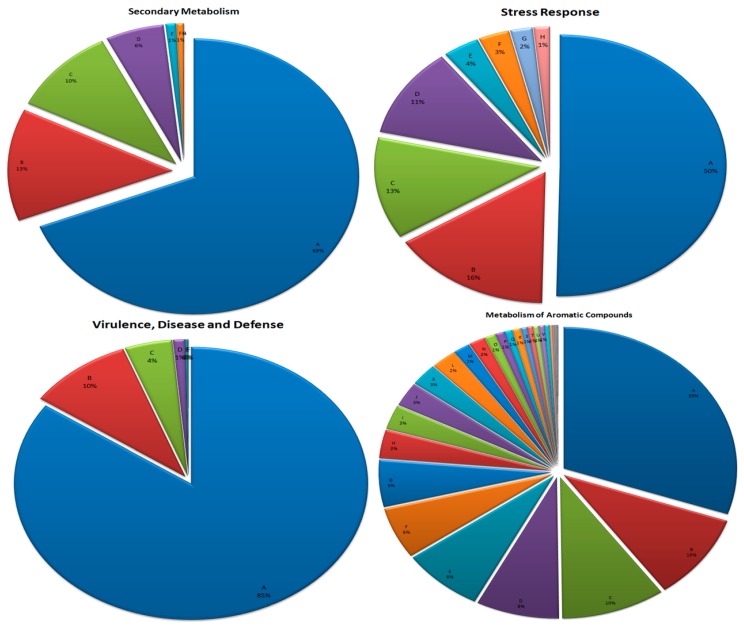
Figure 5.
Assignment of reads in different pathways of the different biological process. Percentage distribution of different pathways in a particular biological process is shown. Abbreviations used are, Secondary Metabolism (A: Plant hormones, B: Bacterial cytostatics, differentiation factors and antibiotics, C: Plant alkaloids, D: Biosynthesis of phenylpropanoids, E: Aromatic amino acids and derivatives, F: Biologically active compounds in metazoan cell defense and differentiation, G: Plant octadecanoids), Virulence, Disease and Defense (A: Resistance to antibiotics and toxic compounds, B: Other, C: Bacteriocins, D: Adhesion, E: Toxins and super-antigens, F: Invasion and intracellular resistance), Stress Response (A: Oxidative stress, B: Osmotic stress, C: Heat shock, D: Others, E: Detoxification, F: Acid stress, G: Cold shock, H: Periplasmic stress), Metabolism of Aromatic Compounds (A: n-Phenylalkanoic acid degradation, B: Phenylacetyl-CoA catabolic pathway (core), C: Anaerobic benzoate metabolism, D: Benzoate transport and degradation cluster, E: Homogentisate pathway of aromatic compound degradation, F: Catechol branch of beta-ketoadipate pathway, G: Protocatechuate branch of beta-ketoadipate pathway, H: Phenylpropanoid compound degradation, I: Central meta-cleavage pathway of aromatic compound degradation, J: 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid catabolic pathway, K: Benzoate degradation, L: Gentisare degradation, M: p-Hydroxybenzoate degradation, N: Biphenyl degradation, O: Chloroaromatic degradation pathway, P: N-heterocyclic aromatic compound_degradation, Q: Acetophenone carboxylase 1, R: Salicylate and gentisate catabolism, S: Carbazol degradation cluster, T: Chlorobenzoate degradation, U: Naphtalene and antracene degradation, V: Aromatic amin catabolism).