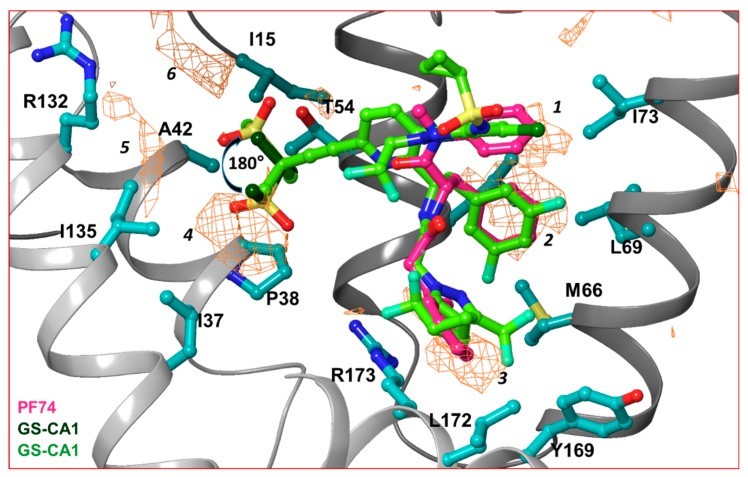
Figure 3.
Hydrophobic pockets between two capsid monomers. This figure shows the hydrophobic pockets (orange wire-mesh) present between two capsid monomers of a hexamer. The amino acid residues that contribute in formation of hydrophobic pockets are displayed in ball-and-stick representation. The presence of hydrophobic pockets 4, 5 and 6 suggests that the conformation of methanesulfonyl moieties of GS-CA1 and GS-6207 can assume a conformation that is 180° rotated from previously predicted [65]. Note that hydrophobic pockets 1, 2 and 3 are at a topologically equivalent position to three ring structures of PF74, GS-CA1 or GS-6207.