Fig. 2.
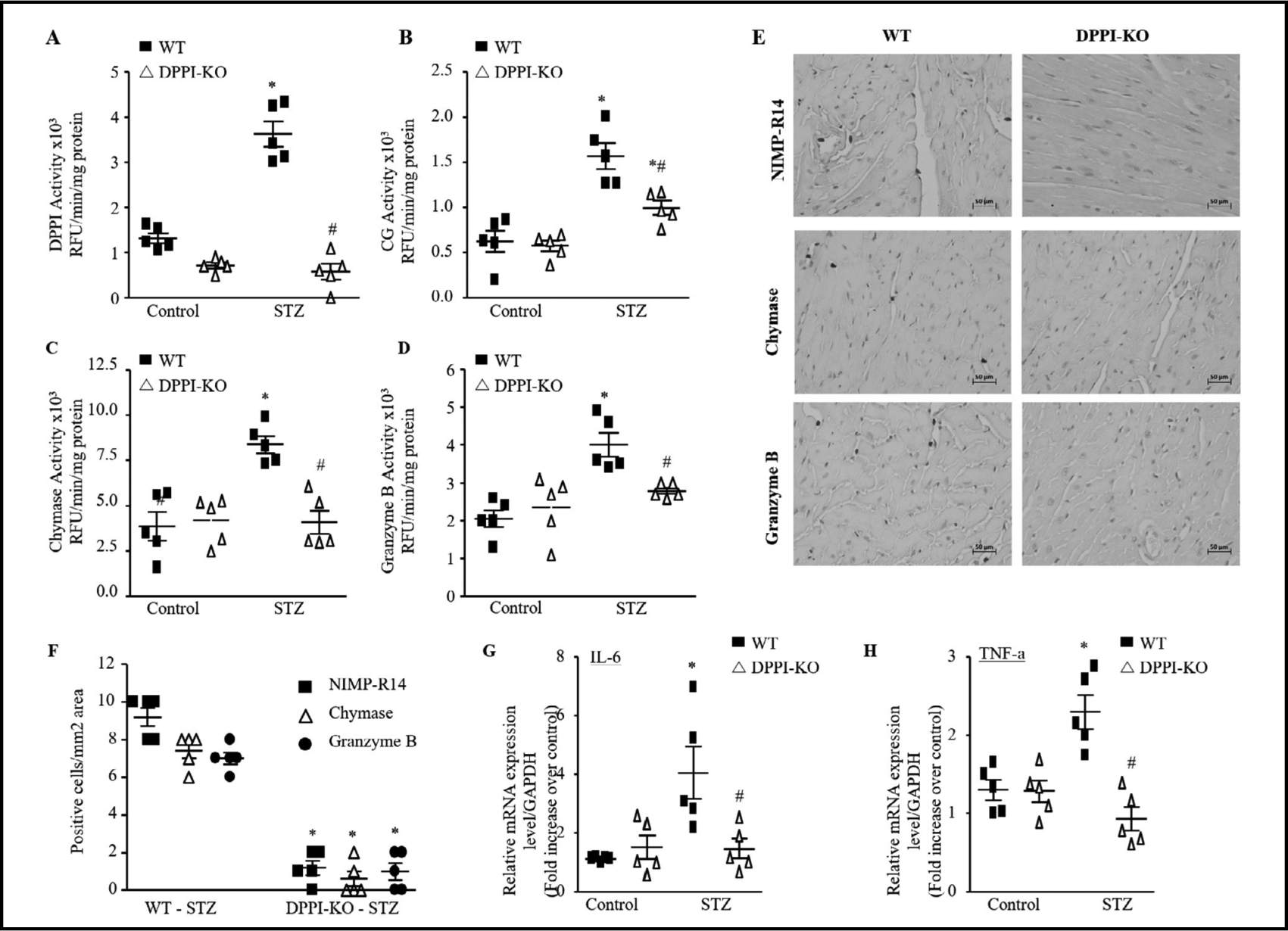
DPPI deletion reduces ISP activity and inflammation after diabetes induction. DPPI (A), cathespin G (CG) (B), chymase (C), and granzyme B (D) activity levels in the left ventricular heart as determined by enzymatic activity assay (n=5 for each group). (E) Representative NIMP-R14, chymase, and granzyme B immunstaining of paraffin-embedded heart sections of WT and DPPI subjected to diabetes induction (400X magnification with scale bars 50 μm). (F) Quantification of NIMP-R14, chymase, and granzyme B-positive cells (n=5 for each groups). Real-time qPCR analysis of IL-6 (G) and TNF-α (H) in controls and after diabetes induction in WT and DPPI-KO mice heart (n=5 for each groups). The data were normalized to GAPDH and were expressed as mean ± SEM. *P<0.05 vs. control, #P<0.05 vs. STZ-treated WT. One-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test was used to compare multiple groups.
