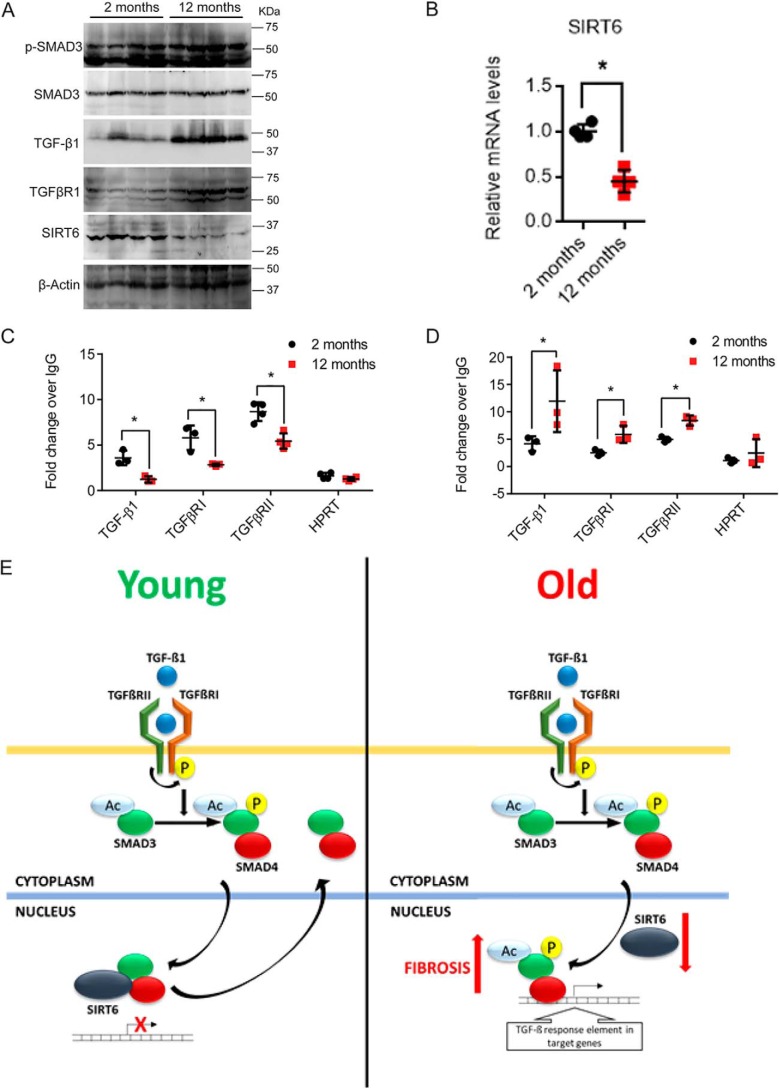
Figure 9.
A, Western blot analysis of heart lysates from 2- and 12-month-old WT mice for the indicated proteins. n = 4. B, scatter plot representing real-time qPCR analysis of SIRT6 in heart samples of 2-month-old and 12-month-old mice. GAPDH was used to normalize the mRNA levels. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (error bars), n = 4; *, p < 0.05. Student's t test was used to calculate the p values. C and D, chromatin immunoprecipitation analysis of heart tissue samples to check for the binding of SMAD3 and SIRT6 to the promoters of the indicated genes in 2-month-old and 12-month-old mice. HPRT was used as the negative control. n = 3–7 mice/group. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. *, p < 0.05. Student's t test was used to calculate the p values. E, representative model depicting the findings of the study. Reduction in levels of SIRT6 with aging results in increased binding of SMAD3 to TGF-β signaling genes, hence leading to enhanced transformation of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts and development of multiorgan fibrosis. SIRT6 acts as a transcriptional repressor of TGF-β/SMAD signaling to regulate the aging-related fibrosis.