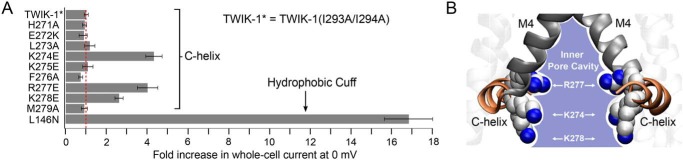
Figure 1.
Role of charged residues within the C-helix. A, -fold-increase in activity of TWIK-1 mutations in the C-helix compared with a mutation within the hydrophobic cuff (L146N). Maximum whole-cell currents were recorded at 0 mV from channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. All mutations were introduced into the TWIK-1* construct, which exhibits greater stability within the plasma membrane. The dotted red line indicates the level of current recorded for WT TWIK-1* (0.8 ± 0.1 μA at 0 mV, n ≥ 18; see also Fig. S1). B, the three activatory mutations within the C-helix are positively charged and point toward the inner mouth of the pore. Mutation of other charged residues that point away does not increase currents.