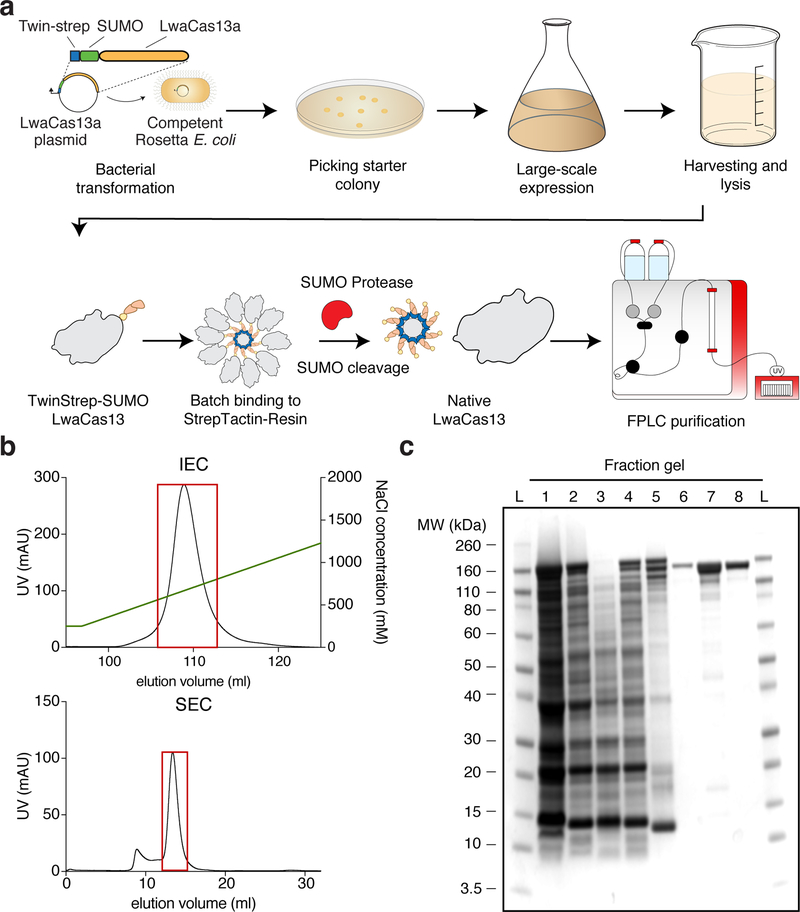
Figure 4: Protein purification workflow and expected results.
(a) LwaCas13a protein expression and purification workflow. The TwinStrep-SUMO-LwaCas13a protein expression plasmid is first transformed into competent Rosetta E. Coli cells. After antibiotic selection and initial growth, expression is induced by IPTG. Following growth, cells are harvested and lysed. The recombinant protein is subsequently enriched from the total cell protein by affinity Streptactin purification. The TwinStrep-SUMO tag is then cleaved by SUMO protease to obtain native LwaCas13 protein. The enzyme is further purified by ion-exchange and size exclusion chromatography on an FPLC system.
(b) FPLC Chromatograms. The graph shows a representative chromatogram of ion-exchange (IEC, top image) and size-exclusion chromatogram (SEC, bottom image) for LwaCas13a. The UV-absorbance in mAU is plotted against the elution volume in mL. The NaCl gradient for ion-exchange chromatography is shown by the green line. The red boxes indicate the protein-containing fractions that were pooled and concentrated.
(c) Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel of protein fraction The progress of protein purification is shown on a Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gel. The fractions are L: Ladder, 1: Cell lysate, 2: Cleared cell lysate, 3: Cell pellet after clearing of lysate, 4: Flow-through following StrepTactin batch-binding, 5: StrepTactin resin before SUMO protease cleavage, 6: Eluted fraction post SUMO protease cleavage, 7: Concentrated sample post ion-exchange chromatography, 8: Final product after size-exclusion chromatography.