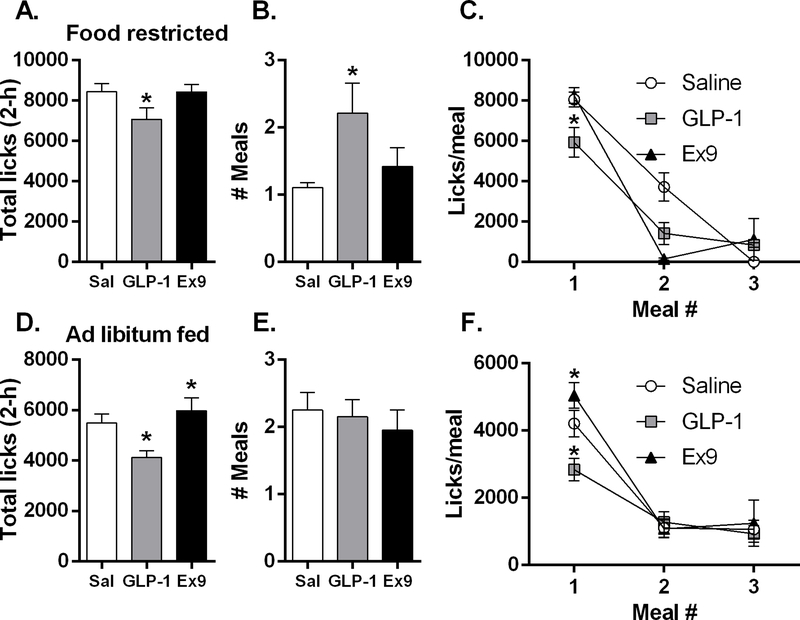
Figure 7.
In food restricted mice (n=19), intra-dLS GLP-1 significantly suppressed both total session licks (A) and the size of the 1st meal (C) while increasing meal number (B), *p<0.05. Under food restriction, 2 of 19 mice in the saline condition, 8 of 19 after GLP-1, and 3 of 19 mice following Ex9 took a second meal of 2 or more bursts; there were no mice that took a third meal after saline, while 3 of 19 after GLP-1 and 2 of 19 mice following Ex9 took a third meal. In ad libitum fed mice (n=20), GLP-1 potently suppressed total session licks (D) and 1st meal size (F) and conversely Ex9 increased both of these variables; there was no effect on meal frequency (E). When fed ad libitum, 13 of 20 mice in the saline condition, 13 of 20 after GLP-1, and 9 of 20 mice following Ex9 took a second meal of 2 or more bursts; there were 9 of 20 mice that took a third meal after saline, while 7 of 20 after GLP-1 and 5 of 19 following Ex9 took a third meal, *p<0.05. All data are shown as mean ± SEM.