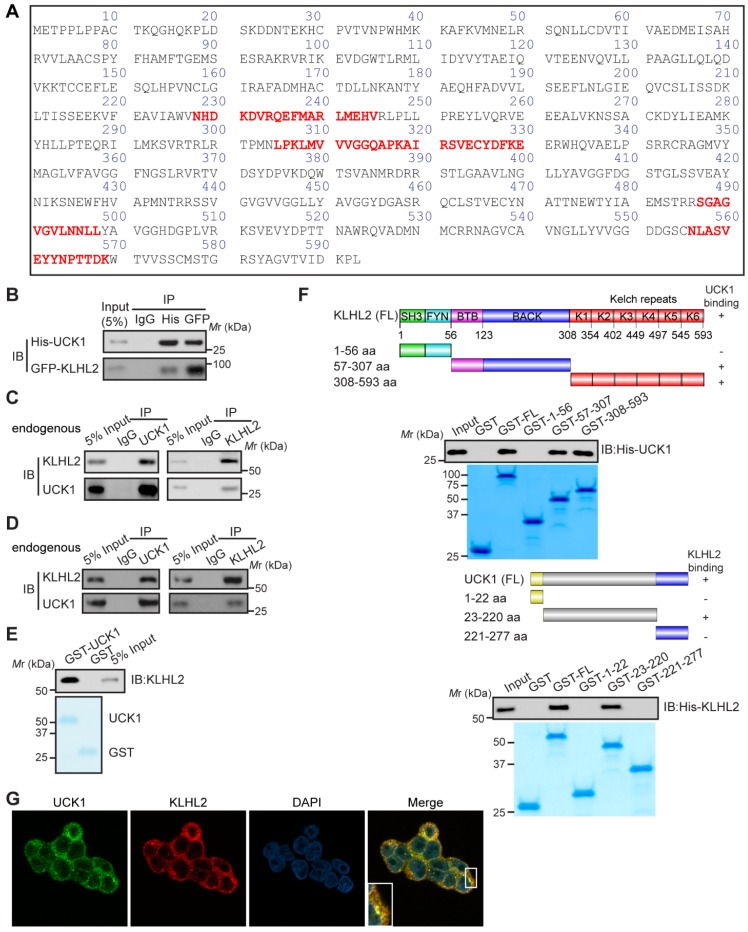
Figure 1.
KLHL2 directly interacts with UCK1 in the cytoplasm. (A) Affinity-purification assay was performed using an anti-Flag-specific antibody and the unique peptides of KLHL2 identified by MS/MS are shown and highlighted in red. (B) HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with His-UCK1 and GFP-KLHL2 for 48 hours. Cell lysates were subjected to indicated immunoprecipitation and subsequent immunoblotting with His or GFP antibodies. (C) HEK293T cells were extracted and immunoprecipitated with an anti-UCK1 (left panel) or anti-KLHL2 (right panel) antibody and probed with indicated antibodies. (D) MV4-11 cells were extracted and immunoprecipitated with an anti-UCK1 (left panel) or anti-KLHL2 (right panel) antibody and probed with indicated antibodies. (E) Recombinant GST-UCK1 protein was incubated with His-tagged KLHL2 protein. Pull-down assay was carried out. (F) Binding of different human KLHL2 truncated fragments to UCK1 as indicated (upper panel). Binding of several different domains of human UCK1 to KLHL2 (lower panel). Numbers represent the amino acid (aa) residues in the various domains of KLHL2 and UCK1, respectively. The interaction between UCK1 and KLHL2 domains is indicated by plus sign (+) while minus sign (-) represents no binding between two proteins. Immunoblotting assay of the interaction between indicated constructs with indicated antibodies. Coomassie blue staining were presented to show expression of GST tagged proteins. (G) Confocal microscopy of HEK293T cells stained with UCK1 and KLHL2 antibodies. DAPI (blue channel) represents nuclear staining. Red, green and blue channel images were captured by Nikon A1 and the Nikon Elements software suite. Maximum projection images were shown and original magnification ×120.