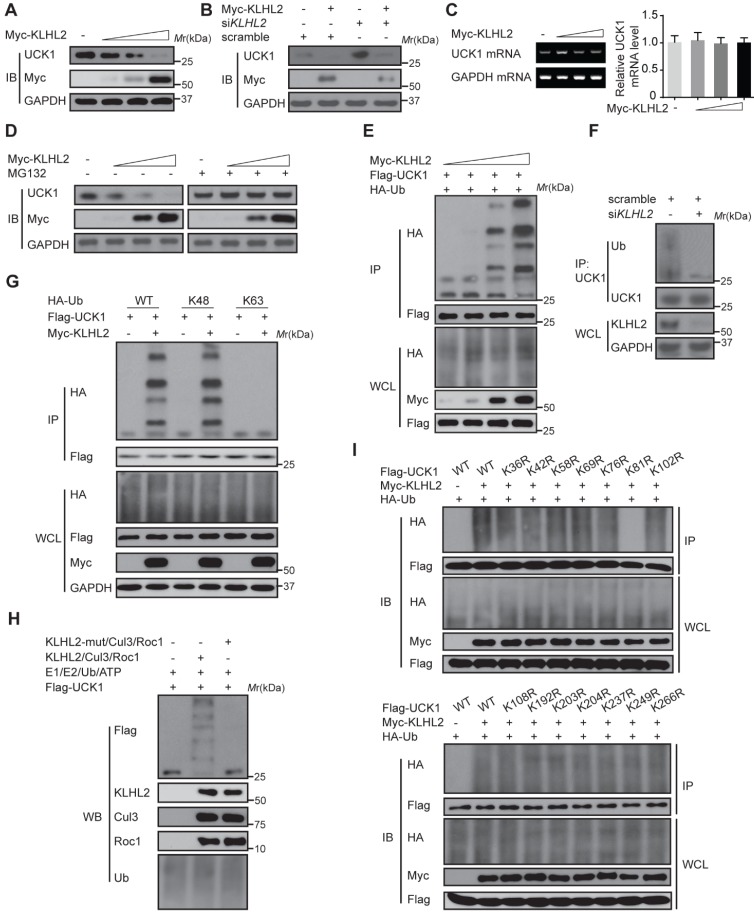
Figure 2.
KLHL2-mediated K48-linked ubiquitination and degradation of UCK1. (A) Immunoblotting assay of UCK1 in HEK293T cells transfected with increasing doses of Myc-KLHL2 plasmids. (B) Immunoblotting analysis of HL-60 cells transfected with KLHL2 plasmids together with KLHL2 siRNA as indicated. (C) qRT-PCR assay of UCK1 mRNA levels in HEK293T cells transfected with increasing doses of KLHL2 plasmids. GAPDH mRNA serves as a loading control. (D) Immunoblotting assay of extracts from HL-60 cells transfected with UCK1 and KLHL2 plasmids and treated with MG132 or dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). (E) Immunoblotting assay of lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with plasmids for Flag-UCK1, HA-ubiquitin and increasing concentrations of Myc-KLHL2 (0, 1, 1.5 and 2 μg), followed by immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag, and analyzed via Immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. Cells were treated with MG132 before harvest. (F) HL-60 cells were transfected with or without KLHL2 siRNA for 48 h. Then cells were treated with MG132 before harvest. Finally immunoprecipitation were conducted and immunoblotting were shown with indicated antibodies. (G) Immunoblotting assay of lysates from HEK293T cells transfected with various combinations of plasmids for Myc-KLHL2, Flag-UCK1, HA-K48-ub and HA-K63-ub and then performed as in E. (H) In vitro ubiquitination assay for UCK1. Flag-UCK1 was subject to ubiquitination in the presence of E1, E2, ATP, and E3 ligase complex. Western blot was performed with antibody as indicated. (I) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting assays of the indicated proteins in HEK293T cells transfected with KLHL2 and K48-linked ubiquitin together with various UCK1 mutants as shown.