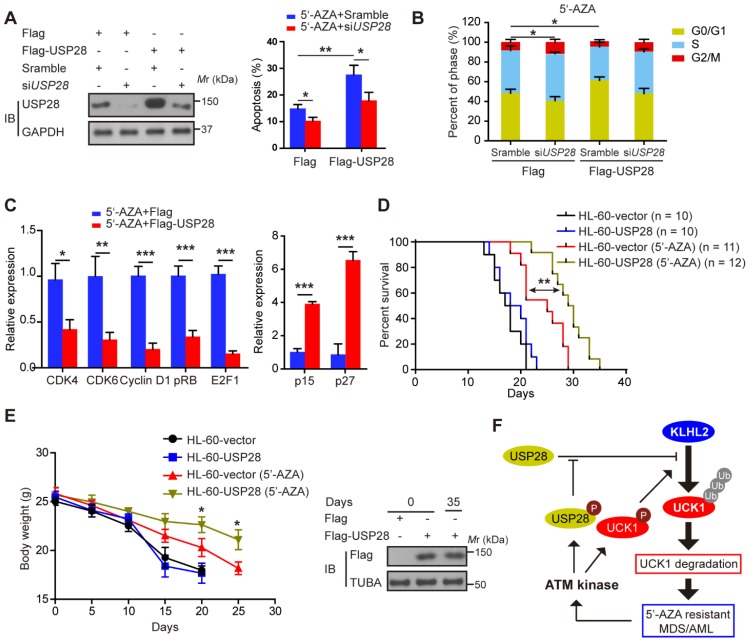
Figure 6.
Ectopic USP28 expression significantly sensitized 5'-AZA to inhibit HL-60 cells in vitro and in vivo. HL-60 cells were divided into HL-60-vector and HL-60-USP28. (A) The cells were treated with 5'-AZA or 5'-AZA plus USP28 siRNA. 24 hours later, the apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry (right panel). Western blots were performed to examine the level of USP28 (left panel). (B) Effects of 5'-AZA on cell cycle progression of HL-60 after USP28 silencing or upregulating. (C) Effects of USP28 overexpression on 5'-AZA-regulated cell cycle-related genes in HL-60 cells which were quantified by qRT-PCR. (D) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for recipients of HL-60 cells with or without USP28 transfection. (E) Left panel: Body weight for AML mice with indicated treatment. Results were expressed as mean ± SEM of at least 10 mice in each group. Right panel: protein samples were extracted from HL-60 cells (the first two lanes) or mouse spleen (the last lane) and then western blot was performed with antibody as indicated. *P < .05; **P < .01 (F) Schematic model indicates that KLHL2/USP28/ATM axis controls UCK1 downregulation which contributes to chemoresistance to 5'-AZA in patients with AML.