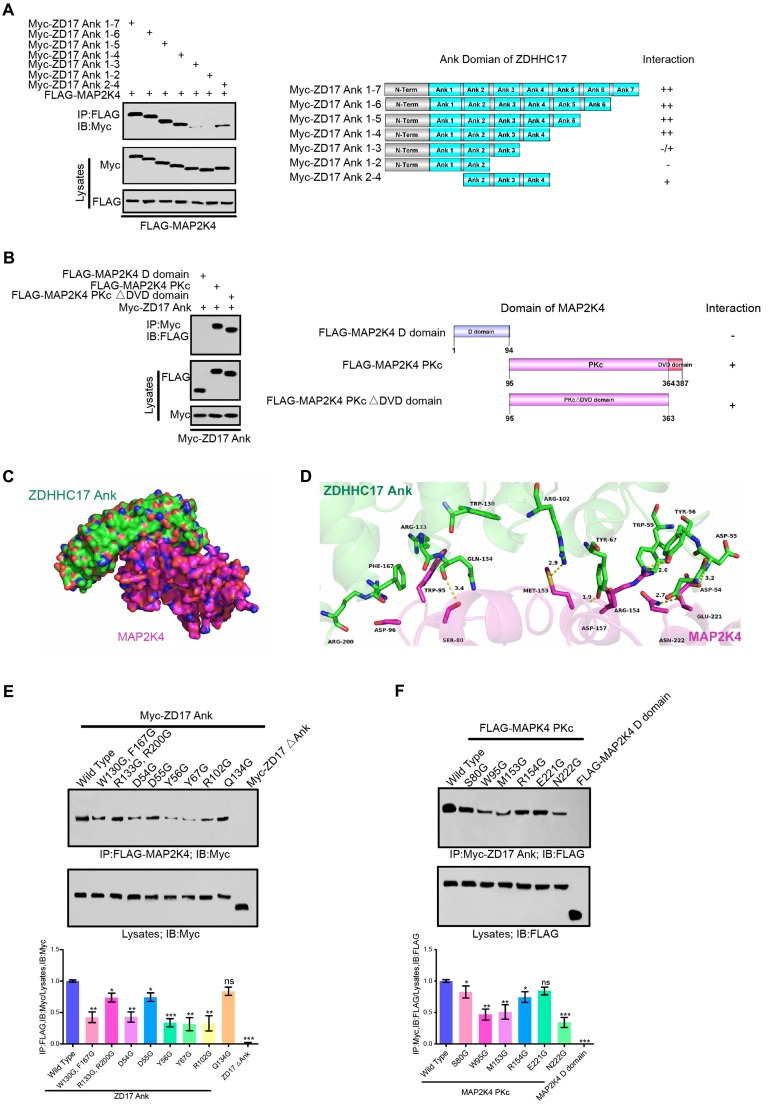
Figure 2.
ZDHHC17 and MAP2K4 Interact Via Specific Binding Motifs. (A) ZDHHC17 ANK (2-4) domain is crucial for ZDHHC17-MAP2K4 interaction. Myc-tagged ZDHHC17 ANK (1-7) and various deletions (right). Interaction capability (positive or negative) is shown. (B) MAP2K4 PKc domain is crucial for the ZDHHC17-MAP2K4 interaction, independent of the DVD domain. FLAG-tagged MAP2K4 and various MAP2K4 deletion fragments (right). Interaction capability (positive or negative) is shown. (C) Surface representation of the complex. ZDHHC17 and MAP2K4 binding mode molecular docking was performed using the ZDOCK server. MAP2K4 (Magenta) binds to the concave ANK(1-7) (Green) region between ANK2 and ANK4. (D) Cartoon and stick representation of ZDHHC17 ANK (1-7) (Pale Green) and ANK (1-7) (Green), respectively. (E) IP of lysates from HEK293 cells expressing Flag-MAP2K4 and Myc-ZDHHC17 ANK (1-7) mutants, followed by IB with anti-Flag antibodies and anti-Myc. Data represent the means ± SD from three separate experiments (ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p <0.01; ***p < 0.001, unpaired t-test). (F) IP of lysates from HEK293 cells expressing FLAG-MAP2K4 mutants and Myc-ZDHHC17, followed by IB with anti-Flag antibodies and anti-Myc. Data represent the means ± SD from three separate experiments (ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, unpaired t-test).