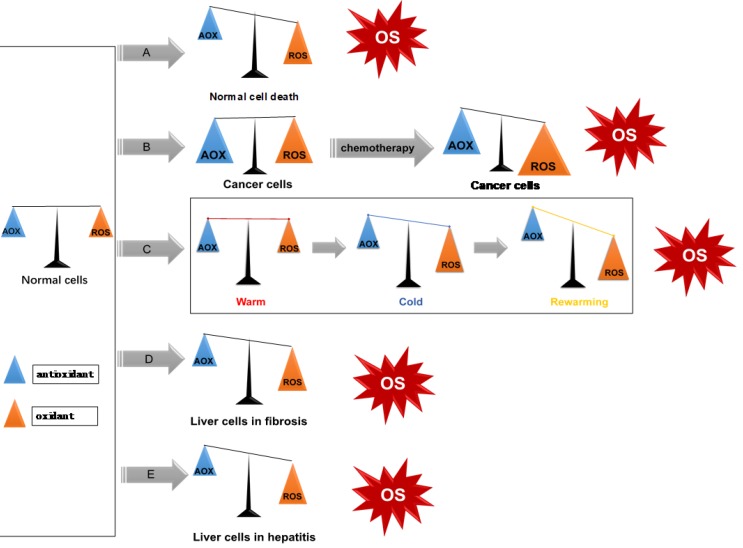
Figure 3.
ROS/redox imbalance in liver diseases. (A) Apoptosis, or programmed cell death; (B) Liver tumor cells have higher oxidation/antioxidant levels, after use of chemotherapy drugs, induces cell death by increasing ROS levels; (C) ROS in liver transplantation. Upon reperfusion, KCs are activated and dramatically release oxygen free radicals, which leads to liver damage; (D-E): HBV and HCV induce chronic hepatitis and liver fibrosis through enhancing oxidative stress response.