Figure 1. Schematic diagram of canonical ERK1/2 signaling.
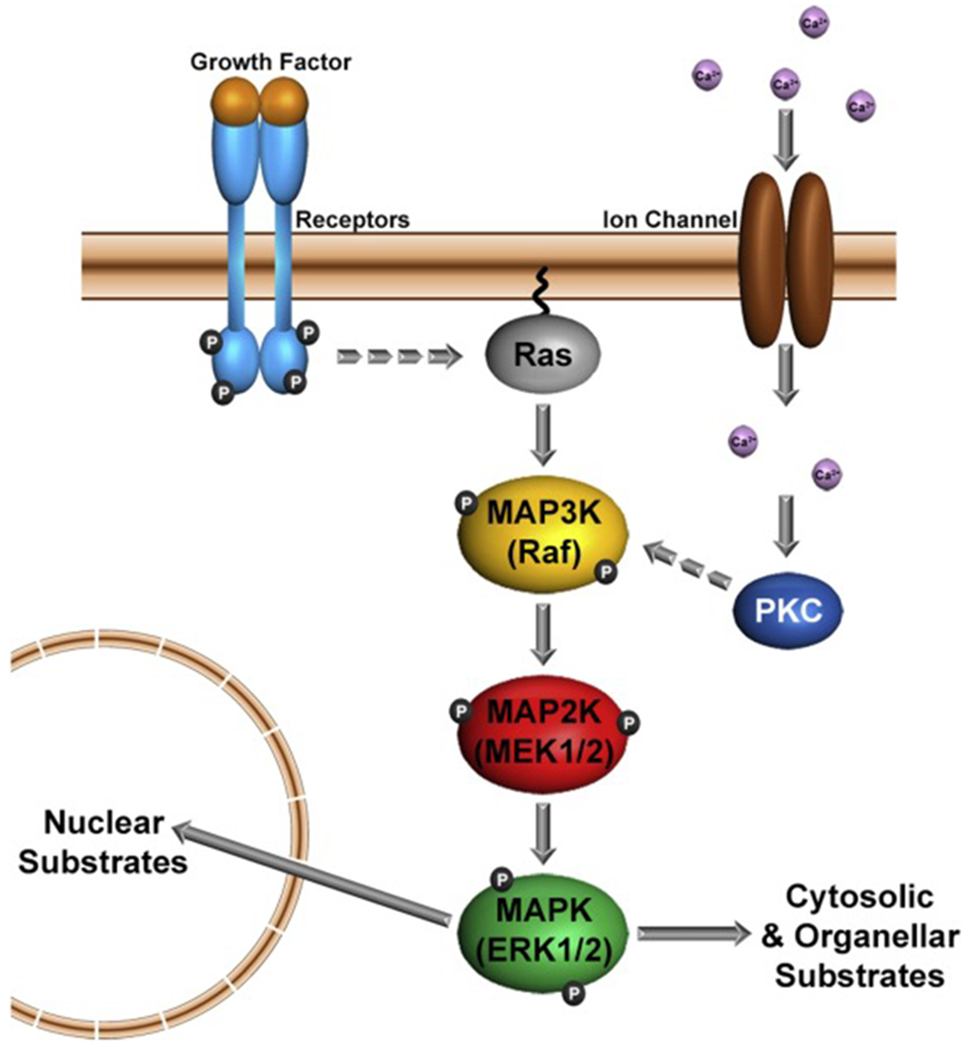
Ligand activation of growth factor receptors at the plasma membrane leads to phosphorylation of their cytoplasmic domains. Adaptor proteins (not depicted) bind to these phosphorylated sites and transduce the signal to small GTP-binding proteins such as Ras (dashed arrow). GTP-Ras, activates the 3-tier MAP kinase module of Raf (MAP3K), MEK1/2 (MAP2K), ERK1/2 (MAPK). Active ERK1/2 (a.k.a. pERK1/2) regulate many cellular processes by phosphorylating target proteins in the nucleus, cytosol and subcellular organelles. A rise in intracellular Ca2+ (lavender spheres) through plasma membrane Ca2+-channels can also lead to activation of the ERK1/2-MAP kinase module via protein kinase C (PKC). For simplicity, other pathways for ERK1/2 activation via integrins or G-protein-coupled receptors are not presented.
