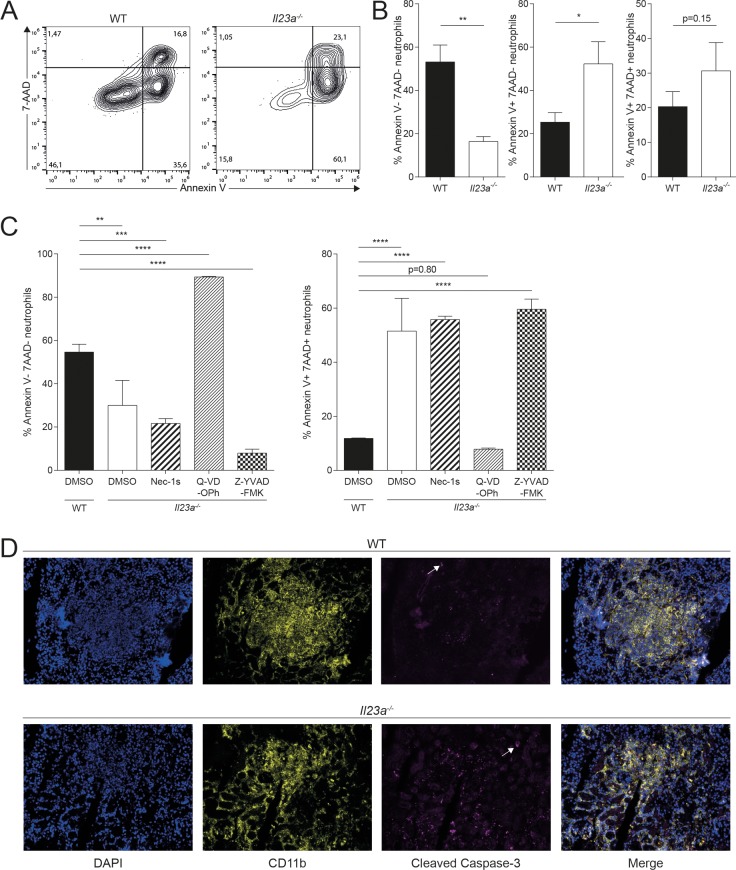
Fig 6. Impaired viability of neutrophils in infected Il23a-/- mice is a consequence of increased apoptosis.
WT and Il23a-/- mice were infected intravenously with 2x105 CFU C. albicans. Kidney neutrophils were isolated by density gradient centrifugation at 24h post infection and cultured in supplemented RPMI 1640 medium for 18h. Viability of neutrophils was assessed by flow cytometry using 7-AAD and Annexin V reagents. (A) Representative FACS plots are pre-gated on neutrophils as shown in Fig 2C without prior exclusion of dead cells. (B) Summary graphs showing the percentage of 7-AAD-Annexin V-, 7-AAD-Annexin V+ and 7-AAD+Annexin V+ populations among total neutrophils. Bars are the mean + SD of each group with n = 3. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Neutrophils were purified from the BM of infected WT and Il23a-/- mice at 24h post infection and cultured with the indicated cell death inhibitors or DMSO as a control in supplemented RPMI 1640 medium for 48h. The cell viability was then assessed as described in (A—B). Summary graphs show the percentage of 7-AAD-Annexin V- and 7-AAD+Annexin V+ populations among total neutrophils. Bars are the mean + SD of each group with n = 3. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) WT and Il23a-/- mice were infected intravenously with 2x105 CFU C. albicans. Sagittal kidney sections were stained 48h post infection for DNA (DAPI; blue), CD11b+ cells (anti-CD11b; yellow) and apoptotic cells (anti-cleaved caspase-3, magenta). Arrows indicate cleaved caspase-3+ cells. Representative images are shown. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Statistics were calculated using unpaired Student’s t-Test (B) or one-way ANOVA (C) as appropriate. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.