Fig. 2. Neural responses to slowed speech demonstrate selective encoding of peakRate events.
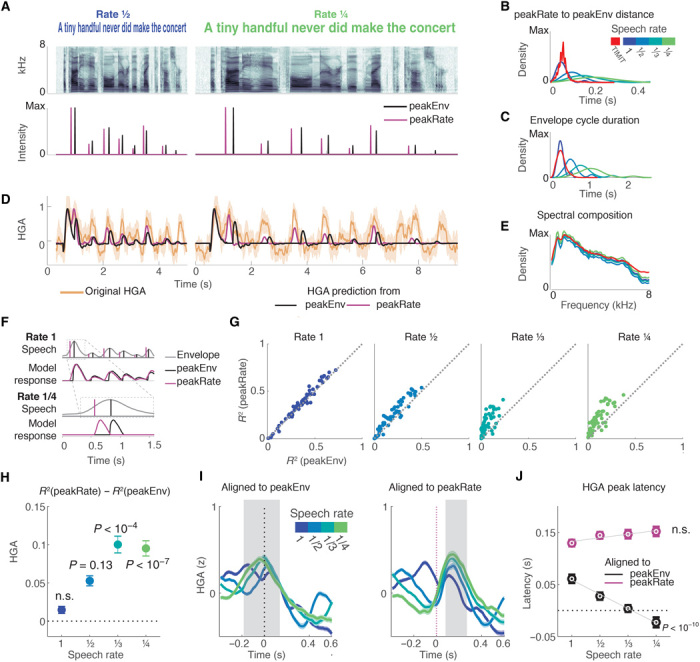
(A) Top: Example sentence spectrogram at slowed speech rates of 1/2 and 1/4. Bottom: Example sentence peakEnv and peakRate events for both speech rates. (B) Distribution of latency between peakRate and subsequent peakEnv events, across all slowed speech task sentences and in full TIMIT stimulus set. Slowing increases time differences, and events become more temporally dissociated. (C) Distribution of envelope cycle durations by speech rate, across all slowed speech task sentences and in full TIMIT stimulus set. Sentence slowing makes envelope cycles more variable, increasing discriminability. (D) HGA response (orange) to an example sentence and neural responses predicted by sparse peakEnv (black) and peakRate (purple) models. Neural responses precede predicted responses of peakEnv model but are aligned with predicted responses of peakRate model accurately. (E) Average spectral composition is similar for stimuli at different speech rates and the full set of TIMIT stimuli. (F) Predicted neural responses for tracking of peakEnv events (black) and peakRate events (purple) for normally paced speech (top) and for slow speech (bottom). At rate 1, the models are indistinguishable. At rate 1/4, the models predict different timing of evoked responses. (G) Comparison of test R2 values for peakRate and peakEnv models by speech rate in all speech-responsive STG electrodes. As speech rate is slowed, peakRate model explains neural responses better than peakEnv model. Each dot represents a single speech-responsive electrode. (H) Mean (SEM) difference in R2 between peakEnv and peakRate models. The peakRate model significantly outperforms the peakEnv model at 1/3 and 1/4 rates. (I) Average HGA after alignment to peakEnv (left) and peakRate (right) events. Gray area marks window of response peaks across all speech rates, relative to event occurrence. When aligned to peakEnv events, response peak timing becomes earlier for slower speech. When aligned to peakRate events, response peak timing remains constant across speech rates. (J) Mean (error bar, SEM across electrodes) HGA peak latency by speech rate and alignment. Speech slowing leads to shortening of the response latency relative to peakEnv events only, such that it occurs before peakEnv events at the slowest speech rate.
