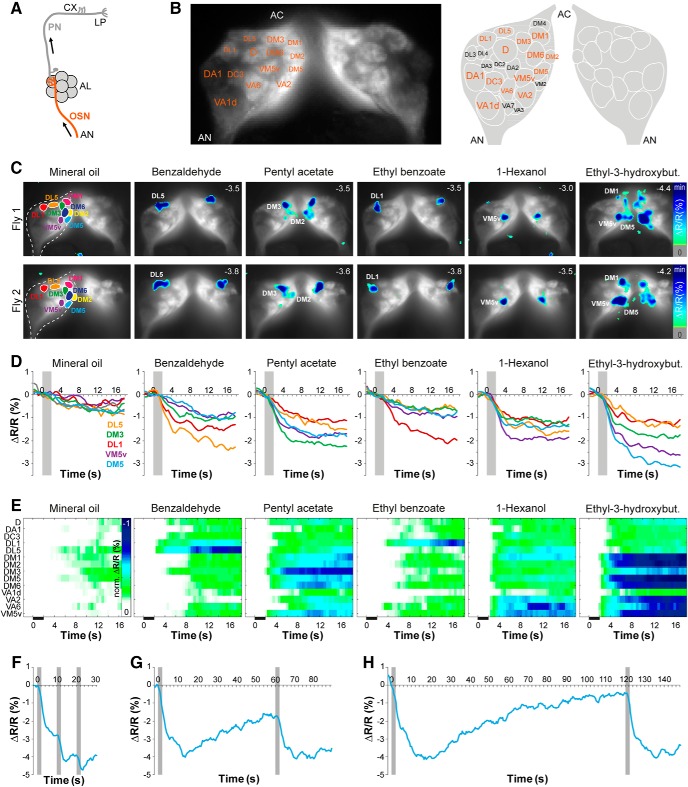
Figure 3.
An odor-specific spatial map of chloride responses in AL sensory neurons. A, Schematic illustrating the expression site of Clomeleon (AL, antennal lobe; AN, antennal nerve; CX, calyx; LP, lateral protocerebrum). B, left, Clomeleon YFP baseline fluorescence in axon termini of OSNs in the AL with anatomic identification of individual glomeruli. Right, Schematic AL map viewed from the angle used for imaging experiments. Glomeruli marked in orange could reliably be identified. AC, antennal commissure. C, Pseudocolor rendering of Cl- responses to different odors and mineral oil in OSN axon termini in the AL of two different individuals. Images represent ΔR/R (%) superimposed onto raw fluorescence images according to the scales on the right. Numbers in each image represent individual fluorescence minimum. Glomerular positions are shown in the first image; glomeruli revealing highest Cl- increase are indicated in each image. The minimum of the scaling is given in each frame in the upper right corner. D, Time courses of Cl- influx for each odor and mineral oil averaged across six to nine animals. Individual glomeruli are indicated by different colors, odor stimulation is marked in gray. E, False color pictures of averaged odor-evoked Cl- signals for 14 glomeruli (42% of all glomeruli labeled by Orco-Gal4) over time across six to nine animals. Clomeleon responses were normalized to highest Cl- influx in each animal over all odors before averaging. Black bar indicates odor application. F–H, Representative time courses of Cl- influx to repeated stimulations of ethyl-3-hydroxybutyrate using interstimulus intervals of 10 s (F), 60 s (G), and 120 s (H). Odor stimulations are marked in gray.