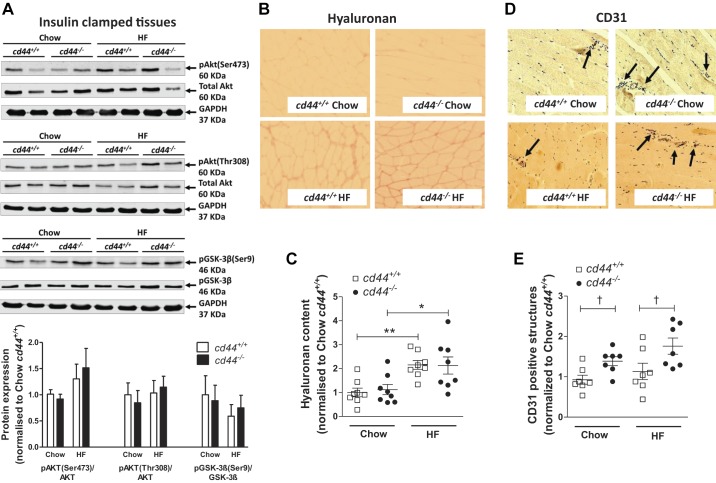
Fig. 4.
Hyaluronan deposition, insulin signaling, and vascularization in gastrocnemius muscle of mice. A–E: gastrocnemius muscle was collected at the end of the hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp, and hyaluronan content and protein expression of CD31 were measured by immunohistochemistry. p-Akt (Ser473 or Thr308)/Akt and p-GSK-3β/GSK-3β were measured by Western blotting. A: representative bands and integrated intensity of respective protein expression when normalized to chow-fed cd44+/+ mice (n = 4–6 male mice). B and C: immunohistochemical detection of hyaluronan was quantified by measuring the integrated intensity of staining. D and E: muscle vascularity was determined by counting CD31-positive structures (denoted by arrows). B and D: representative images (×20 magnification). C and E: quantitative data when normalized to chow-fed cd44+/+ mice (n = 4 female, 3–4 male mice). All data are represented as mean ± SE. Statistical analysis were performed by two-way ANOVA followed by Benferroni post hoc test and unpaired t test as appropriate. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 when compared with chow-fed mice with the same genotype (C). †P < 0.05 when compared with cd44+/+ mice on respective diets (E). HF, high fat.