Fig. 7.
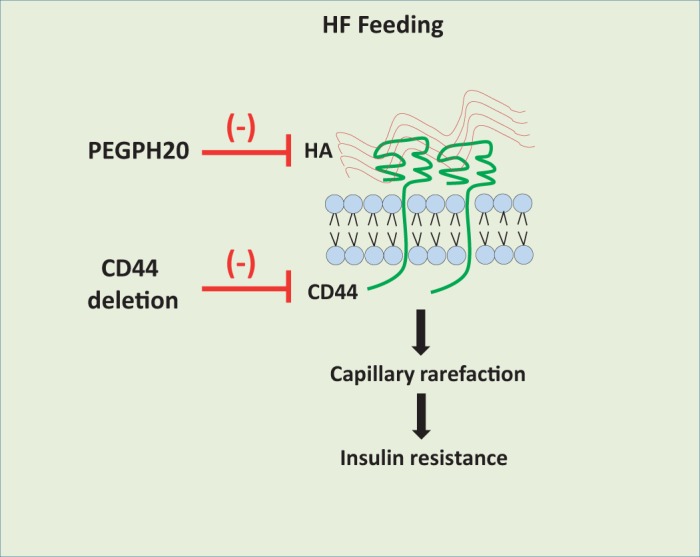
Working model that links hyaluronan-CD44 signaling to skeletal muscle insulin resistance. It is hypothesized that high-fat (HF) feeding in mice increases extracellular matrix hyaluronan (HA) content and CD44 expression, which activates CD44 signaling and causes muscle capillary rarefaction, subsequently leading to the development of insulin resistance. Disruption of this pathway at various steps, such as reduction of hyaluronan by PEGPH20 treatment and/or CD44 deletion, helps in alleviating insulin resistance. Furthermore, PEGPH20 treatment does not further ameliorate insulin resistance post-deletion of CD44, suggesting that hyaluronan is upstream of CD44 and that CD44 is essential for the beneficial effects of PEGPH20. Further investigation using conditional mouse approach will help in identifying CD44 expression site responsible for the beneficial metabolic effects.
