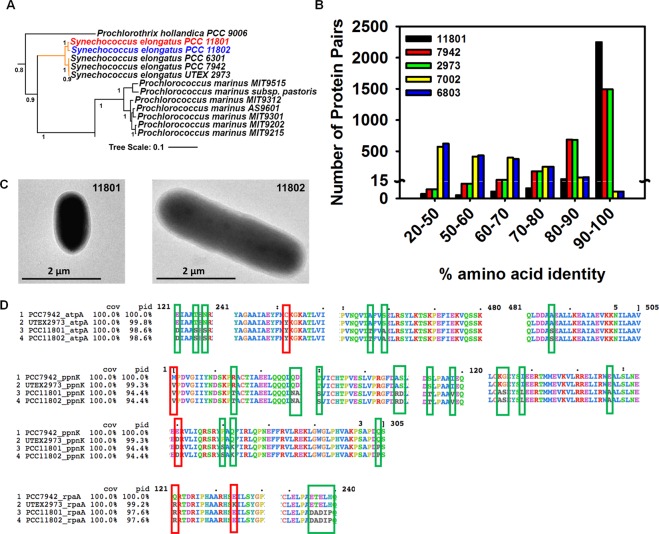
Figure 1.
Identification, phylogenetic assignment, and genome comparison of PCC 11802. (A) A phylogenetic tree created using concatenated protein sequences of 29 constitutive genes showing the completely sequenced organisms in the phylogenetic neighborhood of PCC 11802. A complete tree with 128 cyanobacteria is shown in the supplementary information (Fig. S2). (B) A histogram depicting the level of amino acid identity between shared genes between PCC 11802 genome and the cyanobacterial strains PCC 11801, PCC 7942, UTEX 2973, PCC 7002 and PCC 6803. Only bidirectional best hits were included in the statistics. (C) Cell size comparison of exponentially growing cultures of PCC 11802 and PCC 11801 and (D) Alignment of sequences of proteins, AtpA, PpnK and RpaA showing the amino acid substitutions responsible for fast-growth phenotype and other single amino acid polymorphisms (SAPs) observed in PCC 11802 and 11801 with respect to PCC 7942 and UTEX 2973.