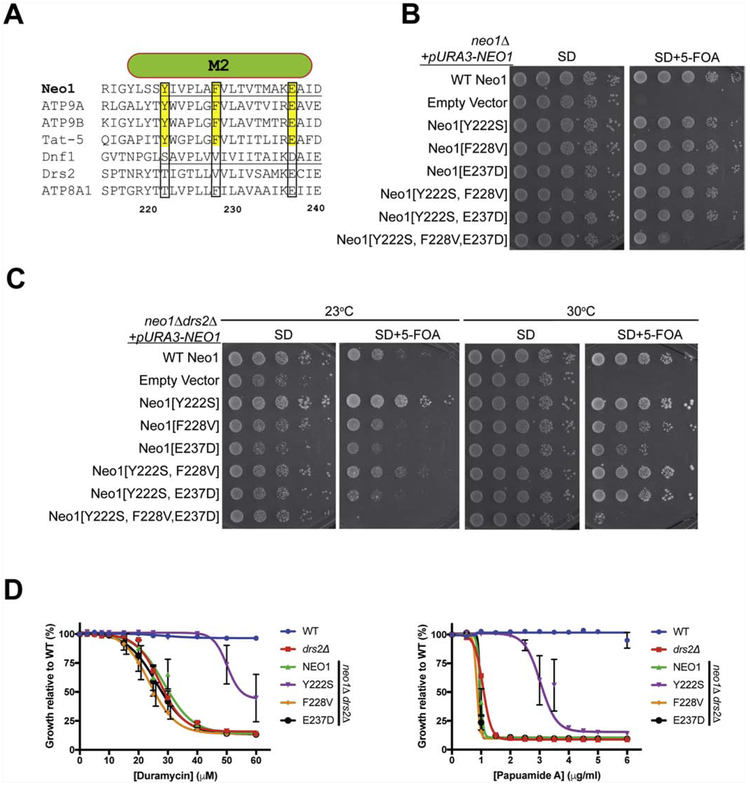
Figure 3. Gain of function and loss of function mutations in M2 of Neo1.
(A) Sequence alignment of transmembrane segment 2 (M2) from divergent P4-ATPases. Numbers are Neo1 residues and targeted residues are boxed. (B) Neo1 mutants Y222S, F228V, E237D and double mutant combinations tested support growth of neo1Δ cells as well as WT Neo1. In contrast, the triple mutant displays a substantial growth defect. (C) Growth of neo1Δ drs2Δ cells expressing Neo1 M2 variants at 23°C and 30°C). Neo1-Y222S improves growth of this strain relative to WT Neo1 while Neo1[E237D] causes a partial growth defect. Y222S suppression of low temperature growth defects is attenuated by F228V and E237D in the double mutants. The Neo1 triple mutant is unable to support growth of this strain. (D) Neo1-Y222S suppresses loss of membrane asymmetry as indicated by increased resistance to duramycin and papuamide relative to WT Neo1. F228V and E237D had no measurable influence on Neo1 activity by these assays.