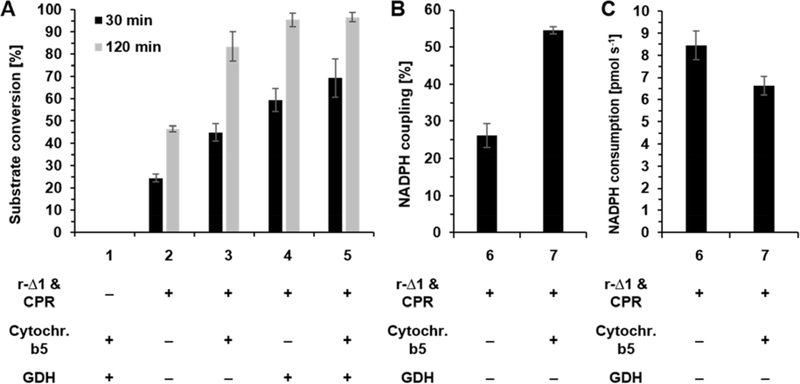
Figure 2.
Lauric acid 4 conversion by rabbit CYP4B1 (r-Δ1). All reactions contained 100 U mL−1 superoxide dismutase and 1,000 U mL−1 catalase. All reactions (except No. 1) also contained 0.25 μM r-Δ1 and 0.5 μM CPR. Where it applies (+), 0.25 μM cytochrome b5 and/or 25 U mL−1 GDH and 20 mM glucose were added. Data represent the average ± standard deviation of three experiments. (A) Influence of cytochrome b5 and cofactor regeneration (GDH) on r-Δ1 activity. NADPH concentration was 200 μM in reactions containing GDH and 1 mM in reactions without GDH. The negative control (reaction 1) did not contain r-Δ1 and CPR. (B) Determination of the NADPH coupling efficiencies and (C) NADPH consumption rates in the presence (+) and absence (−) of cytochrome b5. Reactions 6 and 7 contained equimolar amounts of C12 4 and NADPH (200 μM each).