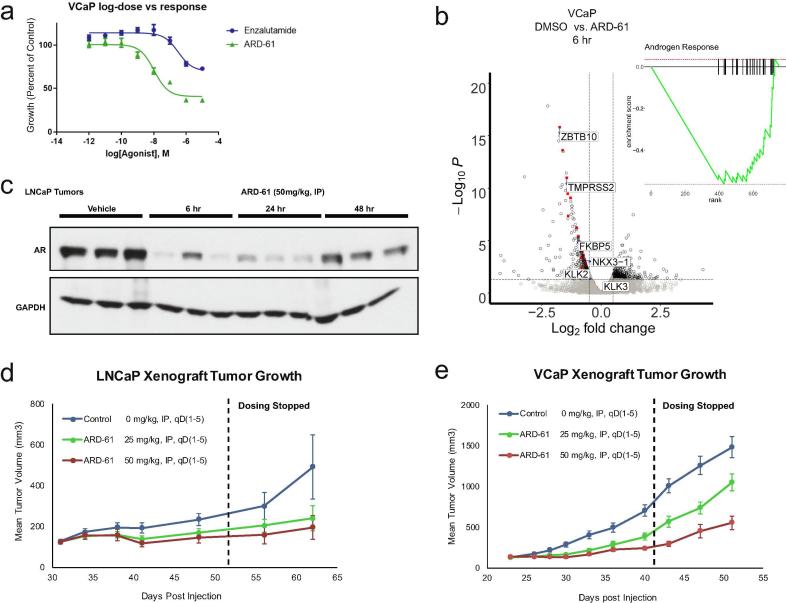
Fig. 2.
ARD-61 decreases AR signaling and inhibits prostate cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. a) Growth curves of VCaP cells assayed by Cell Titer Glo ATP assay® treated with increasing concentrations of ARD-61 and enzalutamide for 5 days (n = 6). b) RNA-sequencing was performed on VCaP cells treated with 100 nM ARD-61 for 6 hr compared to control (DMSO, n = 3). AR target genes, in red with a few representative genes labeled, were significantly downregulated, as illustrated by gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA – inset). c) Western blot of whole tumor lysates from pharmacodynamics studies to confirm ARD-61 induces degradation of AR protein in LNCaP prostate xenograft tumor tissues in intact mice at 6, 24, and 48 hr. Efficacy analysis showed that ARD-61 at 50 and 25 mg/kg, IP, qD, 5 times a week can inhibit tumor growth (n = 10) in both LNCaP (d) and VCaP (e) models (mice intact), even after cessation of dosing (indicated by black dashed line on the graph).