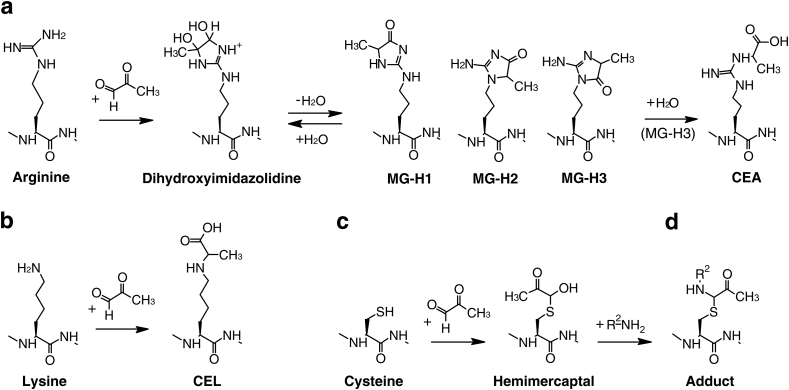
Fig. 1.
MG reaction with amino acid residues of proteins. MG reacts with arginine forming MG-H1, MG-H2 and MG-H3 isoforms, the last of which generates CEA upon hydrolysis (a); MG reacts with lysine forming CEL (b); MG reacts with cysteine forming hemimercaptal (c), which in turn can further react with a free amino (NH2) group forming a stable adduct (d).