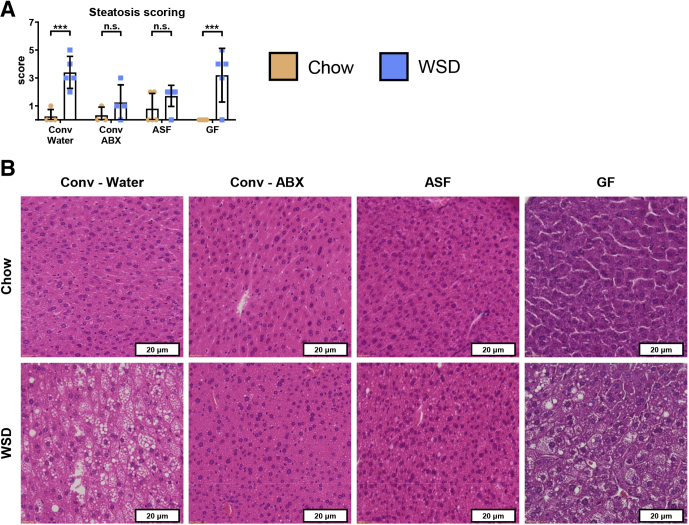
Figure 6.
Hepatic steatosis is reduced in antibiotic-treated and ASF mice on a WSD compared with conventional controls. Extended analysis of mice from Figure 2. Four-week-old male C57BL/6J conventionally raised mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory, 4-week-old male C57BL/6 mice possessing an ASF were obtained from the Georgia State University breeding repository, and 3- to 5-week-old male C57BL/6 GF mice were purchased from Taconic Biosciences. At day 0, animals were switched to a high-fat diet (60% kcal from fat) for 8 weeks or continued on a standard grain-based chow as a control. An additional group of conventional C57BL/6J mice were started on an antibiotic cocktail 3 days before high-fat diet administration and maintained throughout the experiment. At day 56, mice were killed and liver tissues were collected to assess (A) hepatic steatosis and (B) perform H&E staining. Data are the means ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using 1-way analysis of variance corrected for multiple comparisons with a Bonferroni test. ***P ≤ .001. ABX, antibiotic; Conv, conventional; ns, nonsignificant.