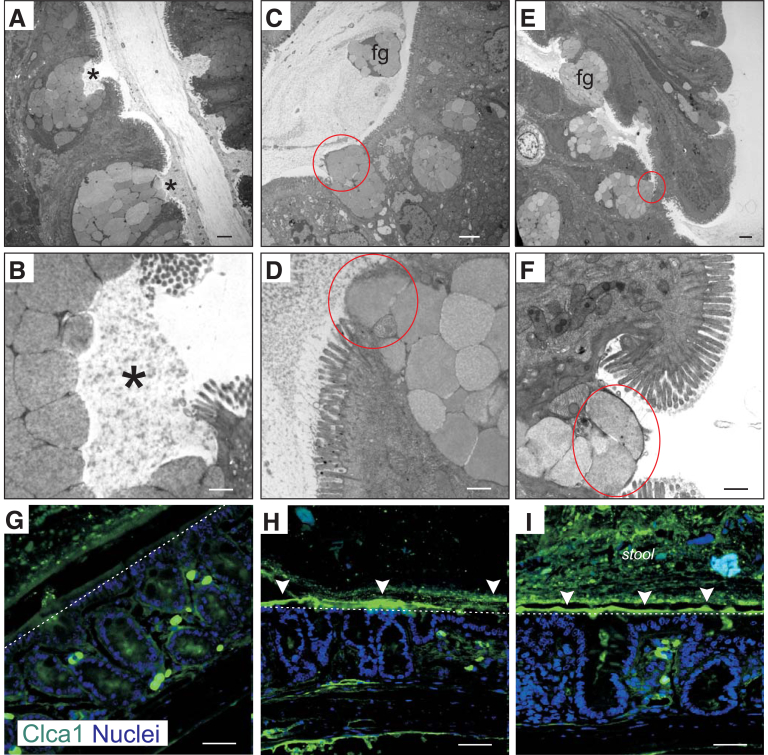
Figure 3.
NKCC1 is required for goblet cells mucus granule exocytosis. Representative transmission electron microscopy images of (A and B) NKCC1WT/WT, (C and D) NKCC1WT/DFX, and (E and F) NKCC1DFX/DFX mouse colon sections. In this experiment, 3 mice per group and 10–20 micrographs per mouse section were analyzed. Stars show the proper release of mucus from goblet cell granules. Red circles highlight improper release of intact mucus granules. Scale bars: (A, C, and E) 2 μm, and (B, D, and F) 500 nm. (G–I) Representative immunostaining of mucus granules with specific protein CLCA1 (green), counterstained with DAPI (blue). Arrowheads indicate accumulation of CLCA1 in the lumen of NKCC1WT/DFX and NKCC1DFX/DFX mouse colons. Dotted lines mark the surface of the epithelium. Fg, floating granules.