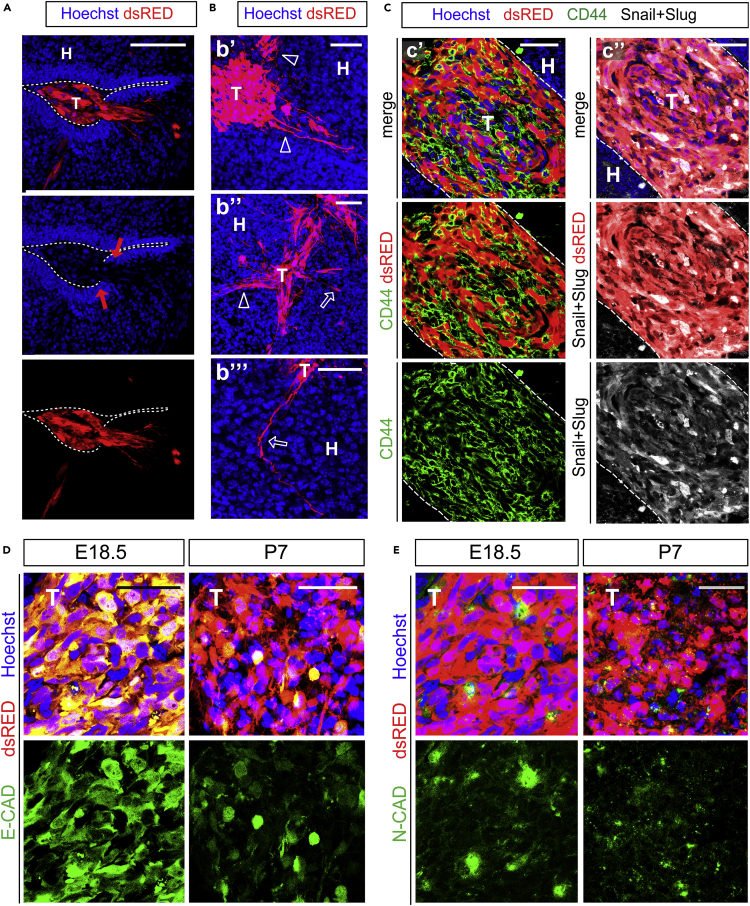
Figure 3.
PDX Show Invasive Growth Pattern and Mesenchymal-like Features in Brains of WT Mice
(A–E) Immunofluorescence images of PDX in cryosections of embryonic mouse brains; blue: Nuclei (Hoechst+), red: patient derived GBM cells. (A) Cross section through a PDX at E18.5; in high magnification showing invading tumor cells (T) inside the host tissue (H); dashed line indicates the host ventricular line border, red arrows: broken apical membrane after tumor cell invasion; scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Cross section through a PDX at E18.5 in high magnification of invading tumor cells (T) inside the host tissue (H), showing infiltrative growth pattern of GBMs. Hollow arrow and hollow arrowheads indicate different routes of invasion; scale bars: 50 μm. (C) Cross section through a PDX at E18.5 showing tumor cells (T) inside the host tissue (H); dashed line indicates the tumor line border in high magnification. Immunostaining for CD44 (C’, green) and Snail + Slug (C’’, white). (D and E) Green: E-CADHERIN (D) or N-CADHERIN (E); cross sections through TX at indicated times showing downregulation of E-CADHERIN and constant expression of N-CADHERIN; scale bars (D and E): 50 μm.