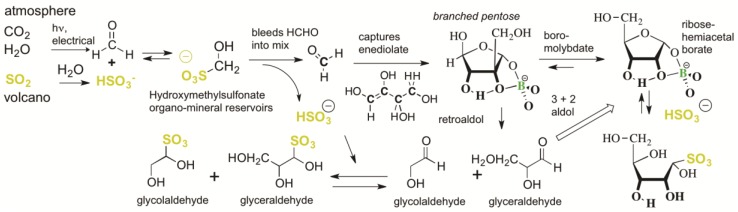
Figure 3.
Unavoidable reactions involving volcanic SO2, HCHO, and other lower carbohydrates in the presence of borate. With each C–C bond formed from a C=O species that comes from a sulfonate, a bisulfite molecule is released. An increasing bisulfite concentration causes the process to be self-limiting; higher and higher concentrations of bisulfite increase the equilibrium levels of unreactive sulfonates. Borate forms a cyclic adduct with the indicated branched pentose, which can undergo a retroaldol reaction to give glycolaldehyde and glyceraldehyde. These can either combine directly to give ribose [42], or can enolize to fix more HCHO in a catalytic cycle [6]. Reaction of bisulfite with ribose competes with ring closure. Thus, bisulfite addition with ribose is less than with HCHO, glycolaldehyde, and glyceraldehyde. The same is the case with ketoses such as xylulose and ribulose. The stereochemistry shown is entirely arbitrary; in the absence of processes for stereo-control, these compounds are made as racemates.