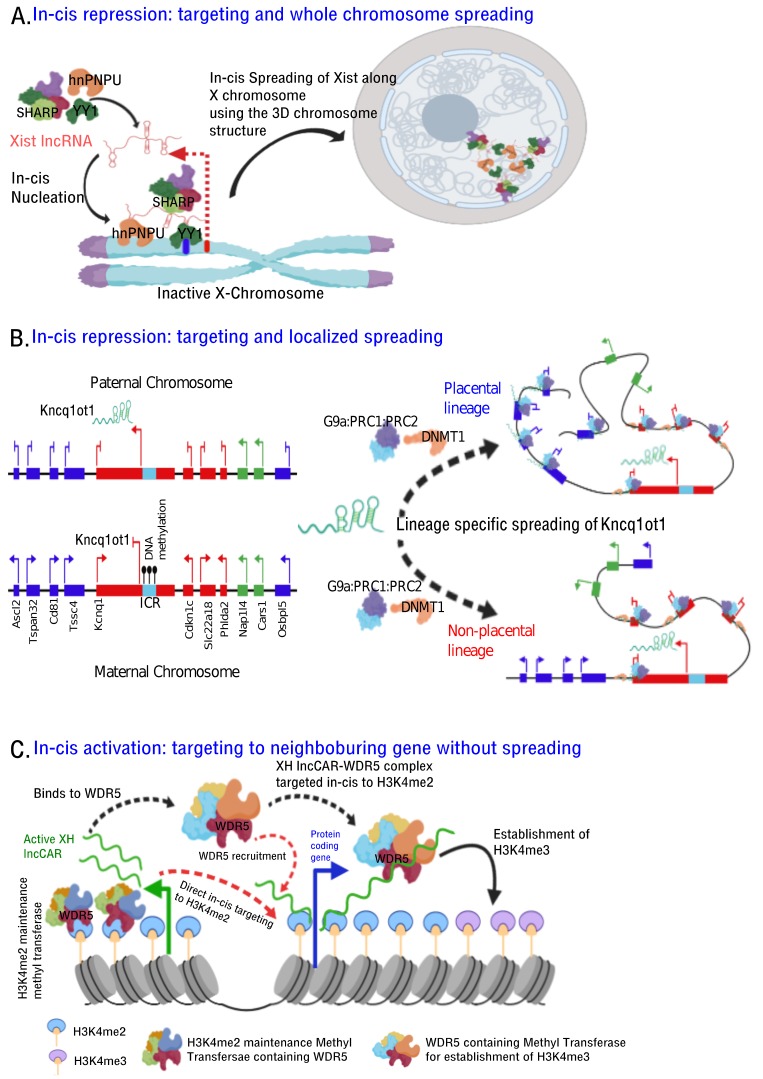
Figure 3.
Mechanism of in-cis chromatin targeting. Proposed model elucidating three different mechanisms of in-cis chromatin targeting of some of the well characterized lncRNAs. (A) Xist lncRNA upon transcription from the X-chromosome (red bar depicts the promoter) that is due to be inactivated, interacts with YY1 protein. YY1, being bifunctional RNA-DNA interacting protein, binds to YY1 binding sites (green bar) downstream of Xist promoter thereby retaining the newly transcribed Xist in cis. hnRNPU is another bifunctional protein, which can interact with both chromatin and RNA, binds at the 5′ end of Xist and targets it to chromatin. Nucleated Xist lncRNA then spreads along the entire X-chromosome using the three-dimensional folding of the chromatin with the aid of other transcriptional repressor complexes such as SHARP and PRC2. (B) Kcnq1ot1 lncRNA is exclusively transcribed (arrows depicting transcription) from an unmethylated paternal ICR (imprinted control region) (sky blue box), located within the intron 10 of its sense partner gene Kcnq1 gene. It functions in-cis to repress (blunted arrows represent transcriptional repression) lineage specific imprinted genes. Kcnq1ot1 (light green) interacts with and recruits G9a-PRC1-PRC2 complex to the promoters of placental linage genes (Blue boxes), while it additionally interacts with DNMT1 and targets G9a-PRC1-PRC2/DNMT1 complex to the promoters of genes that are silenced in all tissues in lineage independent fashion (Red boxes). The targeting and spreading to specific promoters across 1 mega-base region, unlike the whole X-chromosome spreading by Xist, is mediated by the three-dimensional folding of the chromatin. (C) Active XH lncCARs exemplify the case of in-cis targeting of lncRNAs to specific promoter regions of neighbouring protein coding genes to maintain their transcriptional activation. In the model, either the XH lncCARs first binds to WDR5-methyl transferase complex through the RNA binding pocket of WDR5 and then targeted (dashed black arrows) to chromatin at H3K4me2 (WDR5 reads H3K4me2), or they can directly bind H3K4me2 enriched chromatin (dashed red arrows) and act as a scaffold for the efficient docking of WDR5-methyl transferase complex which is necessary to maintain H3K4me2 levels and catalyse the conversion of H3K4me2 to H3K4me3. The maintenance of H3K4me2 marks is possibly mediated by a different WDR5- methyl transferase complex that is independent of the role of XH lncCARs.