FIGURE 4:
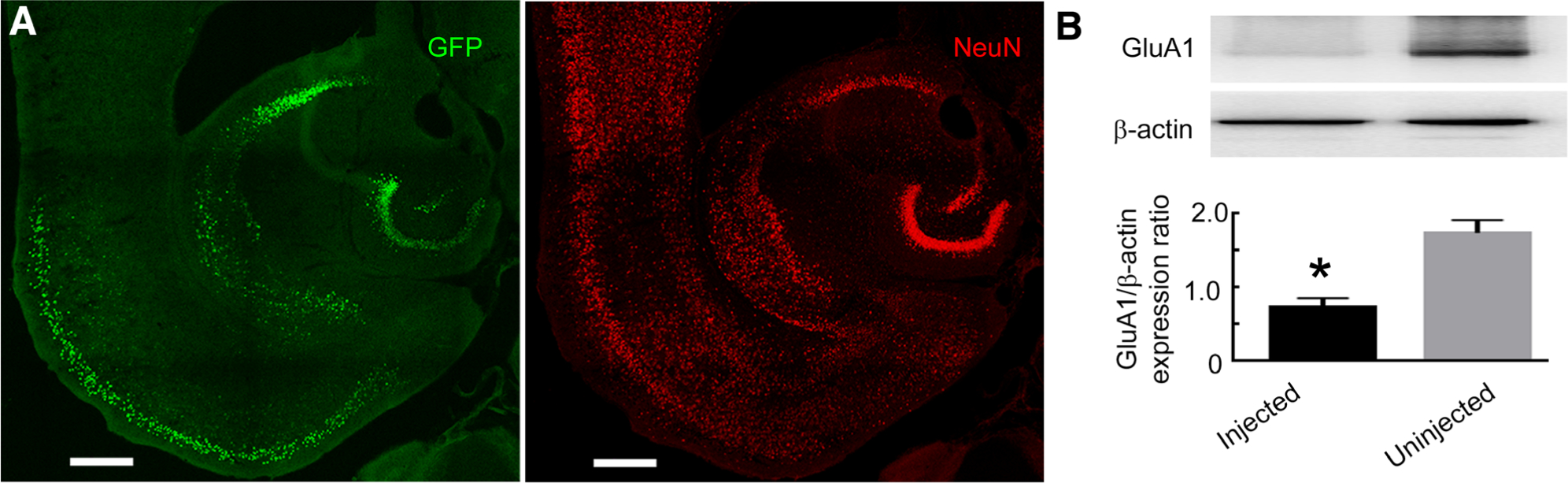
Conditional deletion of the GluA1 subunit using adeno-associated virus (AAV)-expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged CamKII-Cre. (A) Images illustrating GFP expression in the hippocampus of a GluA1-floxed animal injected with AAV serotype 9 expressing a GFP-tagged Cre recombinase under the control of the CamKII promoter. Immunoreactivity of NeuN (red) illustrates the neurons. Colocalization of GFP fluorescence corresponding to Cre expression with NeuN immunoreactivity labeled transduced neurons. The scale bars correspond to 400μm. (B) A Western blot illustrating the expression of the GluA1 subunit in the hippocampal tissue injected with AAV-expressing GFP-tagged CamKII-Cre. The GluA1 subunit expression in the contralateral hippocampus, which was not injected with the AAV, was used as a control. The expression of β-actin was used as a loading control. The graph shows GluA1 to β-actin expression ratio in the injected and uninjected hippocampi. The GluA1 subunit expression in the virus-injected hippocampus was 45 ± 11% of that in the contralateral hemisphere without virus injection (n = 3, *p = 0.0079, t test).
