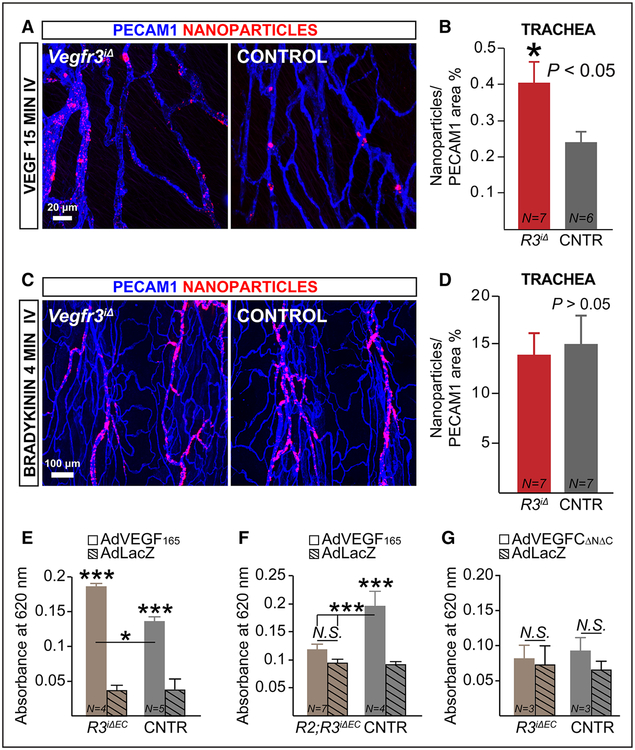
Figure 6. VEGFR3 restricts vascular permeability by suppressing VEGF/VEGFR2 signaling.
A and B, Representative whole-mount images and quantification of nanoparticle (FluoSpheres 0.1 μm) leakage in tracheal blood vessels of adult Vegfr3iΔ (R3iΔ) and control (CNTR) mice 2 wk after tamoxifen administration. The mice received vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) intravenously 15 min before termination. C and D, Vegfr3 loss of function does not affect bradykinin-induced permeability. Representative images and quantification of nanoparticle (0.1 μm) leakage in the tracheas of adult Vegfr3iΔ and CNTR mice 2 wk after tamoxifen administration. The mice received 1 mg/kg bradykinin intravenously, 4 min before termination. E–G, Miles assay of VEGF or VEGFC-induced vascular permeability in Vegfr3iΔEC (R3iΔEC) vs CNTR mice and in compound Vegfr2;Vegfr3iΔEC (R2;R3iΔEC) vs littermate CNTR (Vegfr2flox/flox;Vegfr3flox/flox) 48 h after transduction of the ear skin with the indicated adenoviral vectors. For C–G, the mice were induced at the age of 9 wk with tamoxifen via gavage and analyzed 1 wk thereafter. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001. Error bars, SEM. Numbers (N) are indicated on the bars.