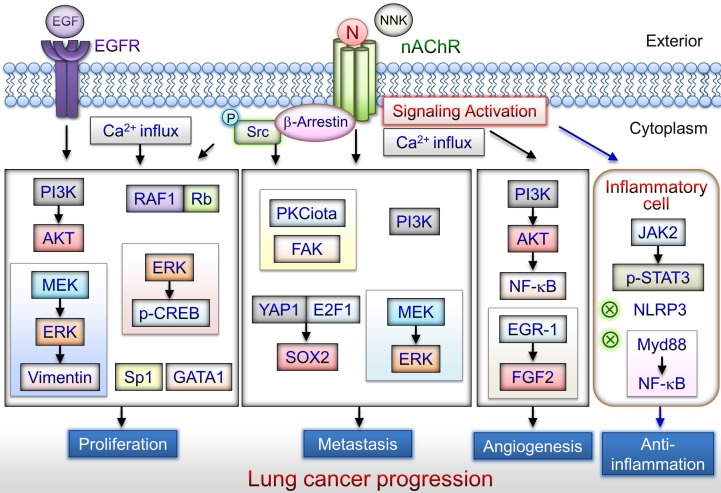
Figure 2.
nAChR-mediated signaling pathways that lead to lung cancer progression. Nicotine/α7nAChR mediates the proliferative effects through several pathways including PI3K/AKT, MEK/ERK, RAF1/Rb, and Sp1/GATA1 activation signaling in lung cancer cells. Cigarette smoking is associated with metastasis of lung cancer. Nicotine/α7nAChR can induce NSCLC cell migration and invasion via the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. NNK enhances lung cancer cell migration via activation of ERK or the Src-PKCiota-FAK signaling axis. Nicotine/α7nAChR can enhance the metastasis of lung cancer cells through activation of the YAP1-E2F1 signaling axis. Moreover, α7nAChR may facilitate lung cancer progression including angiogenesis via the PI3K/AKT or ERG1/FGF2 signaling pathways. α7nAChR-mediated signaling may be a potential target for attenuating the production of inflammatory cytokines in inflammatory cells. Nicotine/nAChR can promote lung cancer development via different signaling pathways. N: nicotine; NNK: 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone.