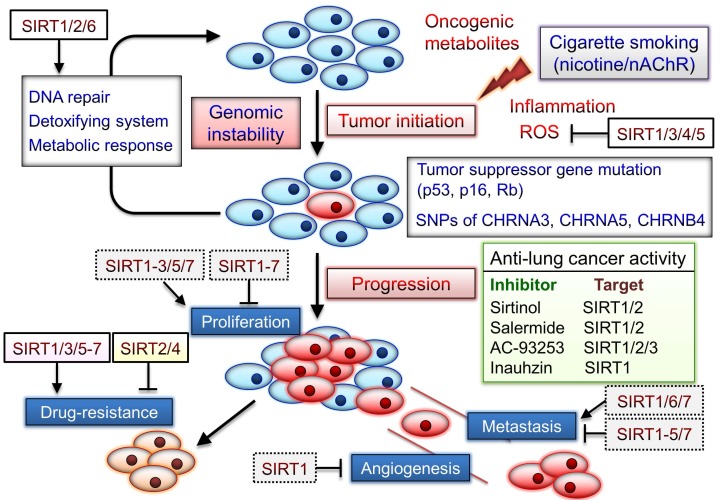
Figure 3.
Roles of sirtuins may be involved in nicotine/nAChR-mediated signaling pathway. Cigarette smoke form carcinogens, including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and the nicotine-derived nitrosamines 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyrydyl)-1-butanone (NNK) and N-nitrosonornicotine (NNN). Tumor suppressor mutations caused by these carcinogens may initiate carcinogenesis. NNK and NNN also significantly contribute to tumor development via activation of nAChRs signaling. SNPs located in a region of chromosome region 15q25 that contains nAChR subunits (CHRNA5, CHRNA3, and CHRNB4) are significantly associated with lung cancer risk. Sirtuins can exert their capacity to respond to environmental changes, and their expression is often altered in cancer. However, the tumor suppressor or promoter role of sirtuins in cancer progression may depend on their tissue- and cancer-specific expression and examined conditions. Several sirtuin inhibitors can suppress lung cancer development and blockade of sirtuins may be a potential anticancer strategy. The dotted box indicated the roles of sirtuins in other cancer types.