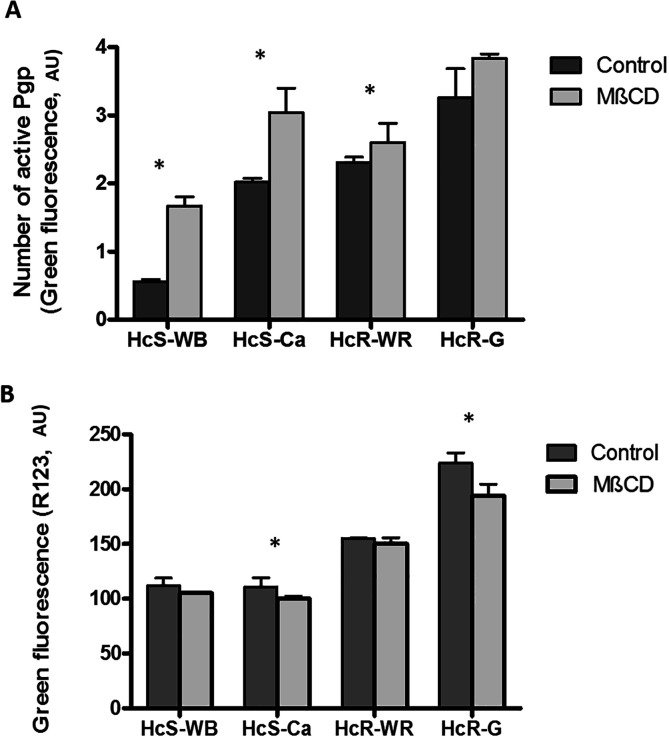
Figure 4.
Quantification and measurement of Pgp activity in nematodes after MβCD (2.25 mM) treatment. (A) Determination of active Pgp in nematode eggs before and after MβCD (2.25 mM) treatment by UIC2 mAb staining. MβCD treatment increased the UIC2 staining significantly for the HcS-WB, HcS-Ca, and HcR-WR isolates after MβCD (2.25 mM) treatment. Mean fluorescence intensity (M ± SD for three measurements). *Significant effect (p < 0.05). (B) Untreated susceptible nematode isolates accumulated significantly less R123 than untreated resistant isolates (p < 0.05). Significant difference of R123 accumulation between susceptible and resistant isolates (p < 0.05). MβCD treatment decreased R123 accumulation, significantly for the HcS-Ca and HcR-G isolates (p < 0.05). Mean fluorescence intensity (M ± SD for three measurements) was estimated from the difference between the native green fluorescence of eggs and that of eggs stained with R123. *Significant effect (p < 0.05). Symbols: (grey rectangles) control eggs and (black rectangles) MβCD treatment. HcS-WB: Haemonchus contortus susceptible Weybridge, HcS-Ca: Haemonchus contortus susceptible Canada, HcR-WR: Haemonchus contortus resistant White River, and HcR-G: Haemonchus contortus resistant Guadeloupe.