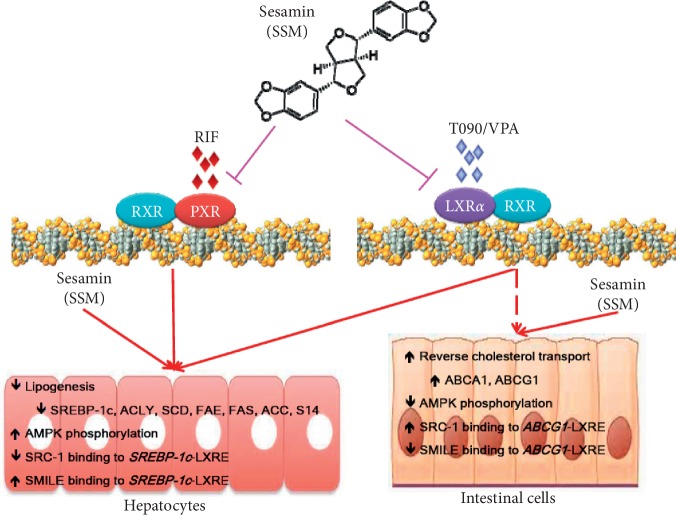
Figure 7.
Schematic model of the LXR pathways in liver and intestinal cells and the action of sesamin on LXRα and PXR. Sesamin selectively reduced hepatic lipogenesis via the inhibition of SREBP-1c expression and its downstream target genes; however, genes involved in RCT of intestinal cells were preserved. It inhibited the hepatic lipogenesis partially via AMPK activation and increased SMILE recruitment to the SREBP-1c promoter. These effects were opposite in intestinal cells, where it did not recruit SMILE but competitively increased SRC-1 binding to the ABCG1 promoter region.