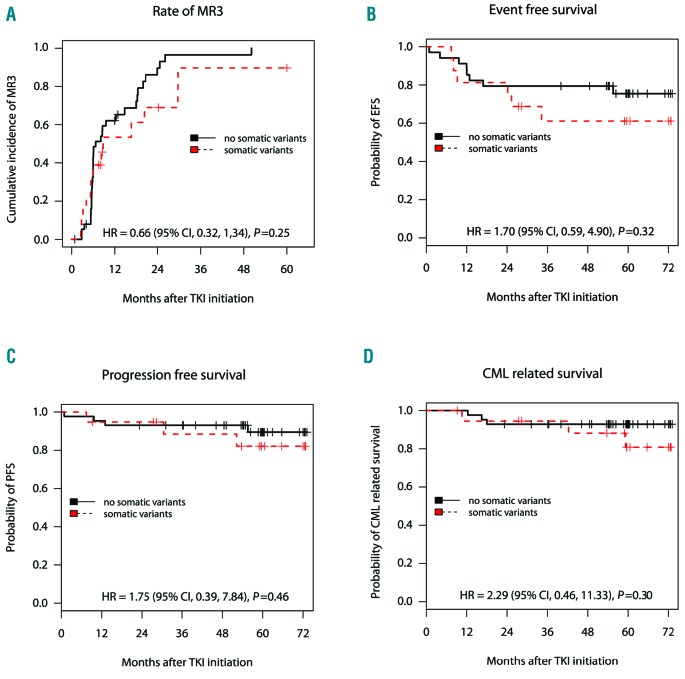
Figure 3.
Association of occurrence of somatic variants with clinical outcome of individuals starting on second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (2G-TKI) treatment. Kaplan-Meier survival analyses in 2G-TKI-treated subjects with somatic variants (red-dashed line) versus non-variant (black-solid line). The end points used were cumulative incidence of major molecular response MR3 at five years (A) and probabilities of event-free survival (EFS) (B), progression-free survival (PFS) (C) and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)-related survival at six years after start of therapy (D). HR (95% CI) derived from Cox proportional hazard regression models and the P-value calculated by the Log Rank test also shown. Number of subjects (N) per group is also shown. Notably, one subject has been excluded from the survival analysis due to non-CML-related death, whereas 12 subjects have been excluded from the EFS and five from the major molecular response (MR3) analyses because of 2G-TKI failure due to intolerance.