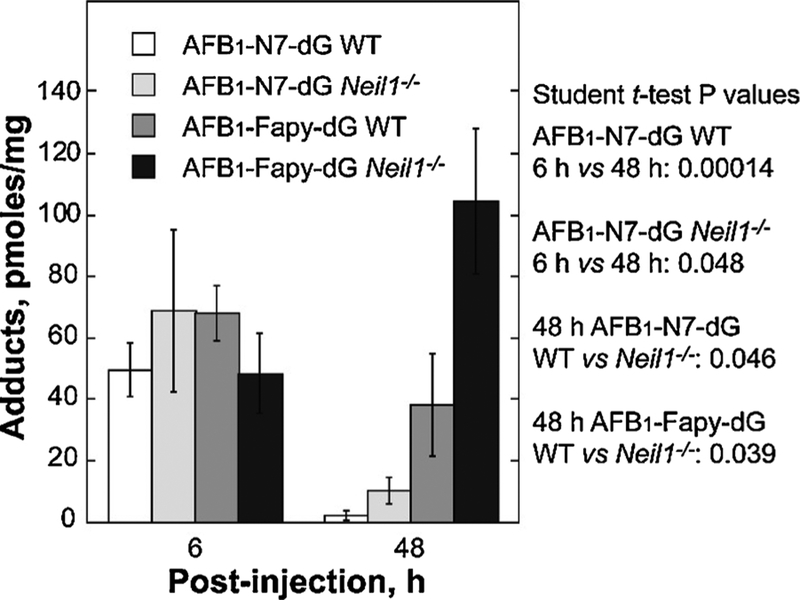
Fig. 5. Levels of AFB1-induced DNA adducts in liver DNA from of WT and Neil1−/− mice following AFB1 IP injection.
Neil1−/− and control WT mice (6 day old pups) were injected with 10 mM AFB1 in DMSO at a dose of 3.5 mg/kg. Livers were harvested at 6 and 48 h post-injection, immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and DNA isolated for AFB1 adduct analysis. Following acid hydrolysis, internal 15N5-guanine-derived standards were added to permit quantitative analysis by isotope dilution mass spectrometry for both AFB1-N7-dG and AFB1-Fapy-dG. Adducts were separated by ultra-performance liquid-chromatography mass spectrometry. The protonated parent ion of the AFB1-N7-dG adduct (m/z 480.1) was selected and subjected to collision-induced fragmentation producing a m/z 152 product ion that was monitored to quantify adduct levels. The AFB1-Fapy-dG adduct was measured by selection of the m/z 498 parent ion and monitoring the collision-induced product ion m/z 452.29. [Reproduced from [76], Fig. 2].