FIGURE 5.
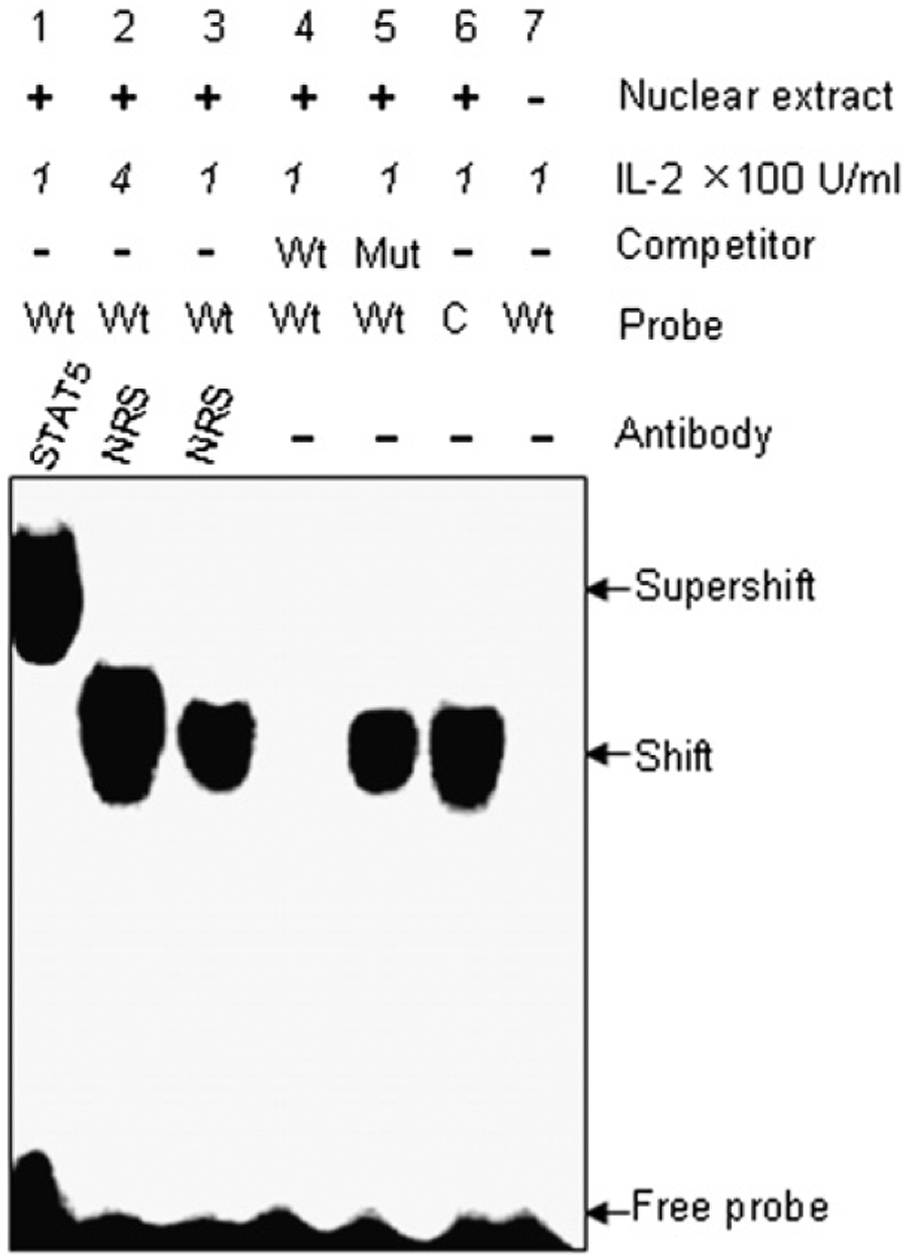
Mutation within the STAT5 binding site abolishes its ability to bind to STAT5. EMSA with the putative STAT5 binding site sequence of the granulysin enhancer was performed. 32P-labeled STAT5 consensus (C) probe (lane 6) and STAT5 wild-type (Wt) probes based on granulysin enhancer sequence (lanes 1–5), were incubated with nuclear extracts from CRL-2105 T cells stimulated with IL-2 at concentration of 100 U/ml or 400 U/ml as indicated. For competition assays, a 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled STAT5 Wt (lane 4), STAT5 mutant (Mut; lane 5) oligonucleotides were incubated with CRL-2105 nuclear extracts prior to incubation with 32P-labeled STAT5 Wt probe. Lane 7, Labeled STAT5 Wt probe without nuclear extract. The labeled STAT5 Wt probe incubated with CRL-2105 nuclear extracts after incubating with 400 U/ml IL-2 (lane 2) or 100 U/ml IL-2 (lane 3). Ab-mediated supershift assays were performed with 2 mg rabbit anti-STAT5 Ab and NRS as a control.
