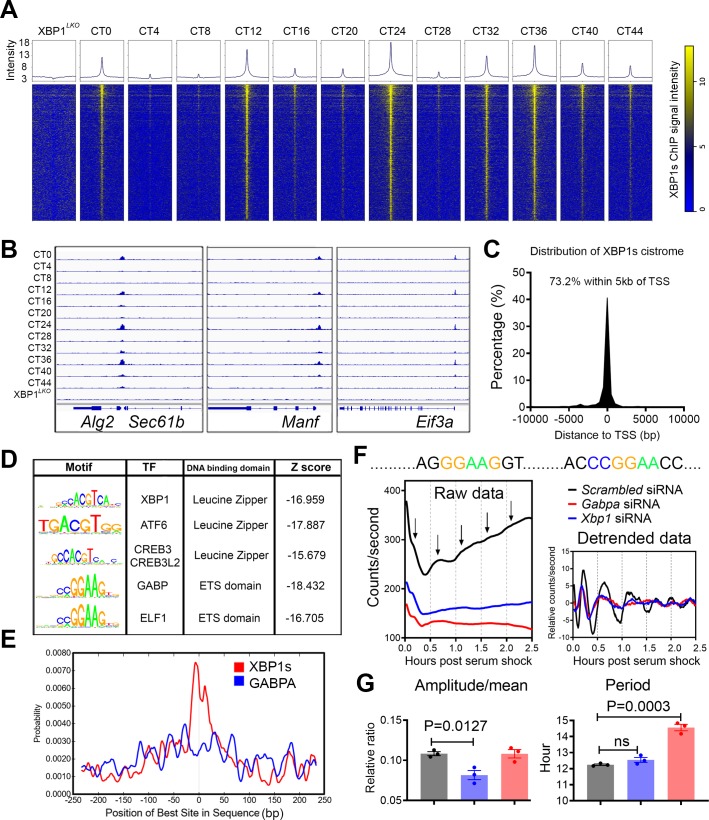
Fig 5. GABPA is a putative new transcriptional regulator of the mammalian 12-h clock.
(A) Heat maps of all XBP1s binding signal at 4-h intervals in XBP1Flox mice as well as in XBP1LKO mice surrounding the center of XBP1s binding sites (±2 kb). (B) Snapshot of target genes selected for alignment of hepatic XBP1s binding sites at different CTs in XBP1Flox and XBP1LKO mice. (C) Distribution of the distance between XBP1s binding sites and the TSS. (D) Top enriched SeqPos motifs common to 12-h cycling XBP1s cistrome. (E) Position distribution of XBP1s or GABPA motifs relative to XBP1s peak center. (F, G) Real-time luminescence analysis of Manf-dluc MEFs post 50% horse serum shock. Consensus GABPA binding sites in the promoter of mouse Manf gene, raw and detrended traces of luminescence recordings from MEFs subject to different siRNA transfection (F) and quantification of relative amplitude and period (G). Data are graphed as mean ± SEM. Numerical values are available in S12 Table and S4 Data except for Fig 5E, which was automatically generated by CentriMo toolbox (version 5.1.0) (http://meme-suite.org/tools/centrimo). ATF6, Activating Transcription Factor 6; CREB3, Cyclic AMP-Responsive Element-Binding protein 3; CT, constant time; ELF1, E74 Like ETS Transcription Factor 1; GABPA, GA-binding protein; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; SeqPos, Sequence Position; siRNA, small interfering RNA; TF, transcription factor; TSS, transcription start site; XBP1s, Spliced Form of X-box Binding Protein 1.