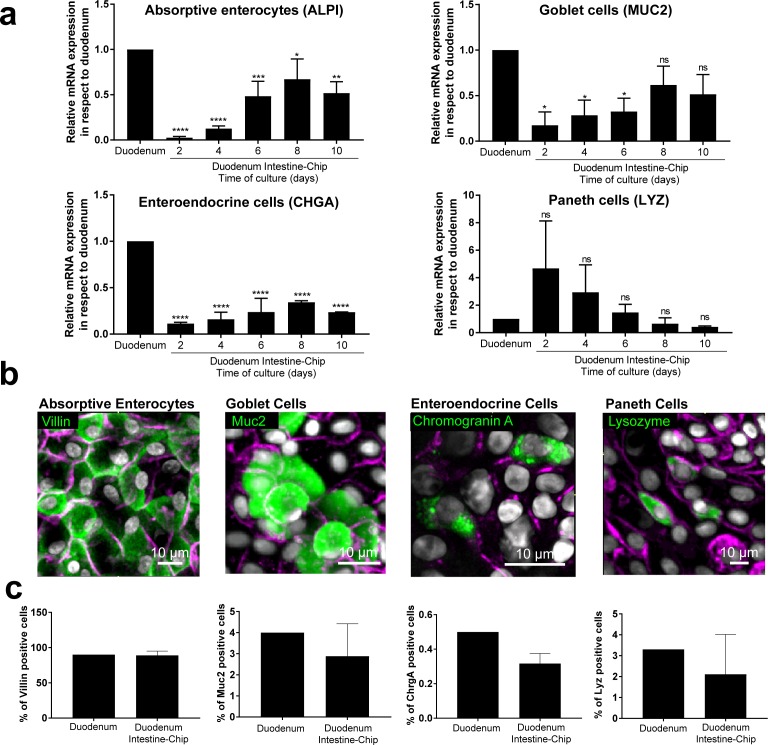
Figure 2. Duodenum Intestine-Chip emulates multi-lineage differentiation of native human intestine.
(a) Comparison of the relative gene expression levels of markers specific for differentiated intestinal cell types, including mucin 2 (MUC2) for goblet cells, alkaline phosphatase (ALPI) for absorptive enterocytes, chromogranin A (CHGA) for enteroendocrine cells, lysozyme (LYZ) for Paneth cells in Duodenum Intestine-Chip and RNA isolated directly from the duodenal tissue (Duodenum). Expression of these genes at different time points (days 2, 4, 6, 8, 10) of Duodenum Intestine-Chip culture is shown. In each graph, values represent average gene expression ± s.e.m (error bars) from three independent experiments, each using different donors of biopsy-derived organoids and at least three different chips per time point. Values are shown relative to duodenal tissue expressed as 1. EPCAM expression is used as normalizing control. One-way ANOVA, ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, ns p>0.05. (b) Representative confocal fluorescent micrographs demonstrating the presence of all major intestinal cell types (green) in Duodenum Intestine-Chip at day 8 of fluidic culture, including goblet cells stained with anti-mucin-2; enteroendocrine cells visualized with anti-chromogranin A, absorptive enterocytes stained with anti-villin and Paneth cells labeled with anti-lysozyme. Cell-cell borders were stained with anti-E-cadherin and are shown in magenta. Cells nuclei are shown in gray. Scale bar, 10 µm. (c) Quantification of the different intestinal epithelial cell types present in Duodenum Intestine-Chip at day eight and identified by immunostaining, as described in (b). Cell ratios are based on 10 different fields of view (10 FOV) counted in three individual chips (each from a different donor) per staining. DAPI staining was used to evaluate the total cell number. Duodenum values, represent cell ratios observed in the histological sections and are based on the literature (Karam, 1999).