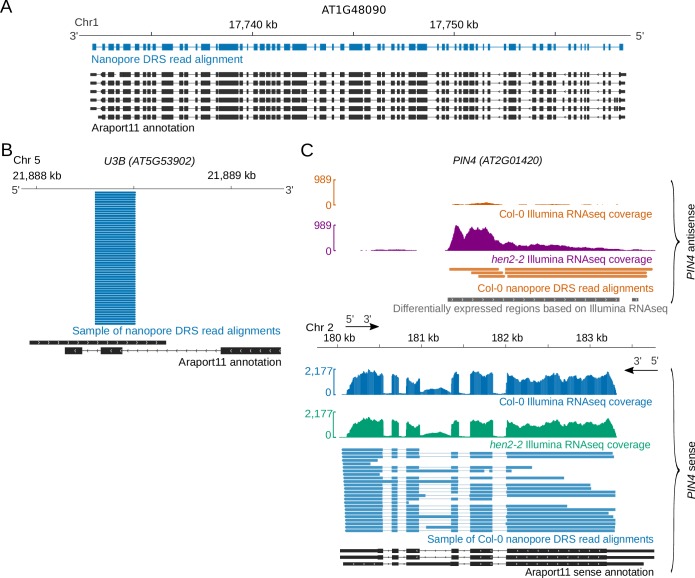
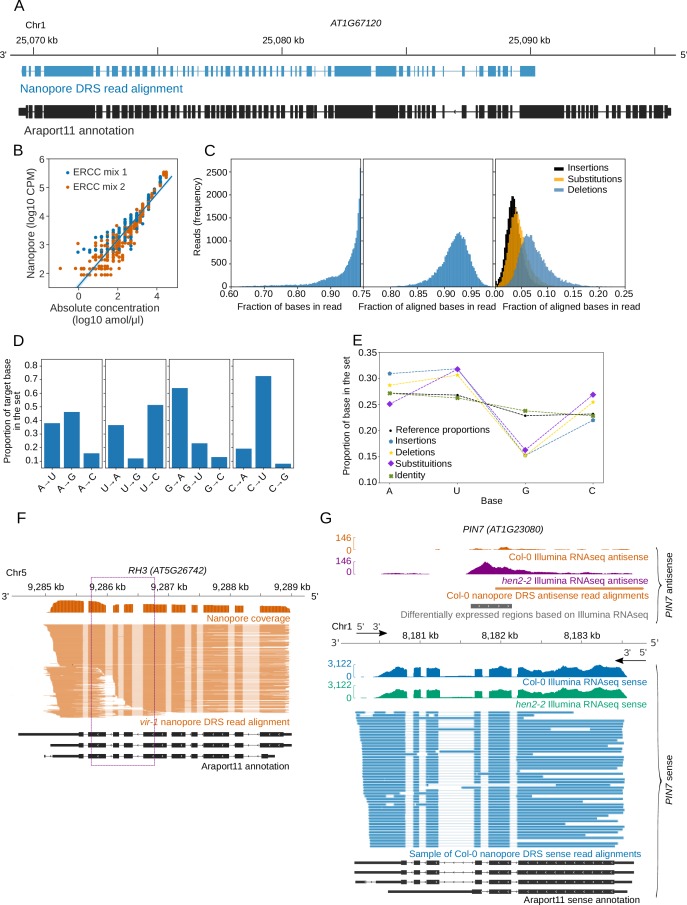
(
A) Nanopore DRS identified a 12.8 kb transcript generated from the
AT1G67120 gene that includes 58 exons. Blue, nanopore DRS isoform; black, Araport11 annotation. (
B) Synthetic ERCC RNA spike-in mixes are detected in a quantitative manner. Absolute concentrations of spike-ins are plotted against counts per million (CPM) reads in log
10 scale. Blue, ERCC RNA spike-in mix 1; orange, ERCC RNA spike-in mix 2. (
C) Overview of the sequencing and alignment characteristics of nanopore DRS data for ERCC RNA spike-ins. Left, distribution of the length fraction of each sequenced read that aligns to the ERCC RNA spike-in reference; centre, distribution of fraction of identity that matches between the sequence of the read and the ERCC RNA spike-in reference for the aligned portion of each read; right, distributions of the occurrence of insertions (black), substitutions (orange) and deletions (blue) as a proportion of the number of aligned bases in each read. (
D) Substitution preference for each nucleotide (left to right: adenine [A], uracil [U], guanine [G], cytosine [C]). When substituted, G is replaced with A in more than 63% of its substitutions, while C is replaced by U in 73%. Conversely, U is rarely replaced with G (12%) and A is rarely substituted with C (16%). (
E) Nucleotide representation within the ERCC RNA Spike-In reference sequences (black dots) compared with nucleotide representation within four categories from the nanopore DRS reads. Identity matches between the sequence of the read and the ERCC RNA spike-in reference (green crosses), insertions (blue pentagons), deletions (yellow stars) and substitutions (purple diamonds).G is under-represented and U is over-represented for all three categories of error (insertion, deletion and substitution) relative to the reference nucleotide distribution. C is over-represented in deletions and substitutions. A is over-represented in insertions and deletions and under-represented in substitutions. (
F) Signals originating from the
RH3 transcripts are susceptible to systematic over-splitting around exons 7–9 (highlighted using a purple dashed box), resulting in reads with apparently novel 5′ or 3′ positions. This appears only to occur at high frequency in datasets collected after May 2018 (
Supplementary file 1) and may result from an update to the MinKNOW software. (
G)
PIN7 antisense RNAs detected using nanopore DRS. Blue, Col-0
PIN7 sense Illumina RNAseq coverage and nanopore
PIN7 sense read alignments; orange, Col-0
PIN7 antisense Illumina RNAseq coverage and nanopore
PIN7 antisense read alignments; green,
hen2–two mutant
PIN7 sense Illumina RNAseq coverage; purple,
hen2–two mutant
PIN7 antisense Illumina RNAseq coverage; black,
PIN7 sense RNA isoforms found in Araport11 annotation; grey,
PIN7 antisense differentially expressed regions detected with DERfinder.