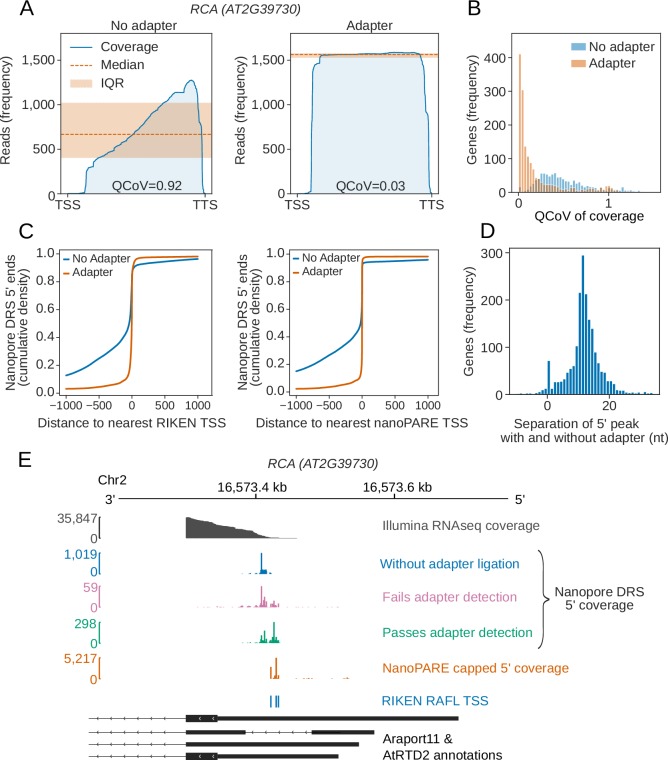
Figure 3. Cap-dependent ligation of an adapter enables detection of authentic RNA 5′ ends.
(A) 5′ adapter RNA ligation reduces 3′ bias in nanopore DRS data at RCA (AT2G39730) from 0.92 to 0.03. Blue line, exonic read coverage at RCA for reads without (left) and with adapter (right); orange line, median coverage; orange shaded area, interquartile range (IQR). Change in 3′ bias can be measured using the IQR/median = quartile coefficient of variation (QCoV). (B) 5′ adapter RNA ligation reduces 3′ bias in nanopore DRS data. Histogram showing the QCoV in per base coverage for each gene in the Araport11 annotation, for reads with a 5′ adapter RNA (orange), and reads without a 5′ adapter RNA (blue). (C) Cap-dependent adapter ligation allows identification of authentic 5′ ends using nanopore DRS. The cumulative distribution function shows the distance to the nearest Transcription Start Site (TSS) identified from full-length transcripts cloned as part of the RIKEN RAFL project (left), or 5’ tag identified from nanoPARE data (right), for reads with a 5′ adapter RNA (orange) compared with reads without a 5′ adapter RNA (blue). (D) Cap-dependent adapter ligation enabled resolution of an additional 11 nt of sequence at the RNA 5′ end. Histogram showing the nucleotide shift in the largest peak of 5′ coverage for each gene in data obtained using protocols with vs without a 5′ adapter RNA ligation. (E) For RCA (AT2G39730), the 5′ end identified using cap-dependent 5′ adapter RNA ligation protocol was consistent with Illumina RNAseq and full-length cDNA start site data but differed from the 5′ ends in the Araport11 and AtRTD2 annotations. Grey, Illumina RNAseq coverage; blue, nanopore DRS 5′ end coverage generated without a cap-dependent ligation protocol; green/pink, nanopore DRS 5′ end coverage for read alignments generated using the cap-dependent ligation protocol with (green) and without (pink) 5′ adapter RNA; orange, 5’ coverage of nanoPARE data; blue, TSSs identified from full-length transcripts cloned as part of the RIKEN RAFL project; black, Araport11 and AtRTD2 annotations (with duplicated 5’ positions removed).