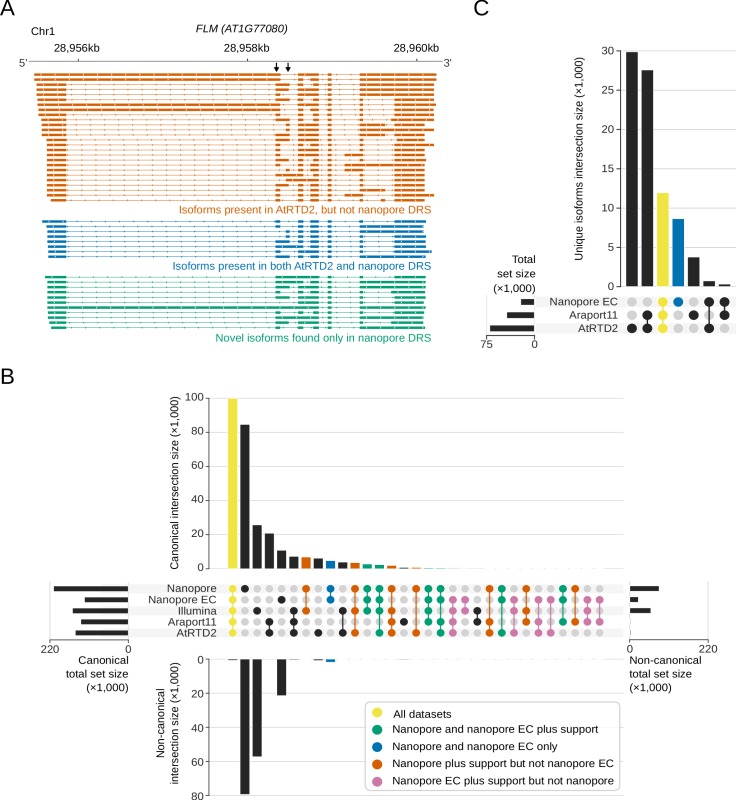
Figure 4. Nanopore DRS reveals the complexity of alternative splicing.
(A) Nanopore DRS identified the mutually exclusive alternative splicing of the second and third exons of FLOWERING LOCUS M (FLM, AT1G77080) and several novel isoforms. Black arrows indicate mutually exclusive exons. Orange, isoforms present in the AtRTD2 annotation but not identified using nanopore DRS; blue, isoforms common to both AtRTD2 and nanopore DRS; green, novel isoforms identified in nanopore DRS. (B) Comparison of splicing events identified in error-corrected and non-error-corrected nanopore DRS, Illumina RNA sequencing, and Araport11 and AtRTD2 annotations. Bar size represents the number of unique splicing events common to the set intersection highlighted using circles (see Supplementary file 5 for the exact values). GU/AG splicing events are shown on the top and non-GU/AG on the bottom of the plot: yellow, splicing events common to all five datasets; green, events common to both error-corrected and non-error-corrected nanopore DRS with support in orthogonal datasets; blue, events common to both nanopore DRS datasets without orthogonal support; orange, events found in uncorrected nanopore DRS (but not error corrected) with orthogonal support; pink, events found in error-corrected nanopore DRS (but not uncorrected) with orthogonal support. (C) Comparison of RNA isoforms (defined as sets of co-spliced introns) identified in error-corrected full-length nanopore DRS, Araport11 and AtRTD2 annotations. Bar size represents the number of splicing events common to a group highlighted using circles below (see Supplementary file 5 for the exact values): yellow, unique splicing patterns found in nanopore DRS and both reference annotations; blue, novel isoforms found only in nanopore DRS.