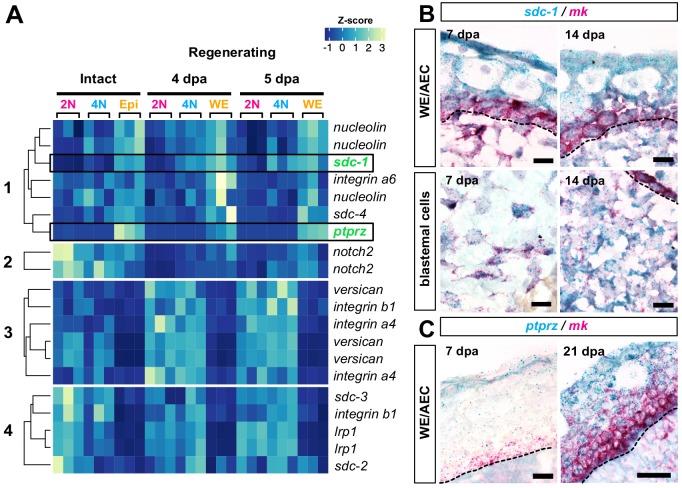
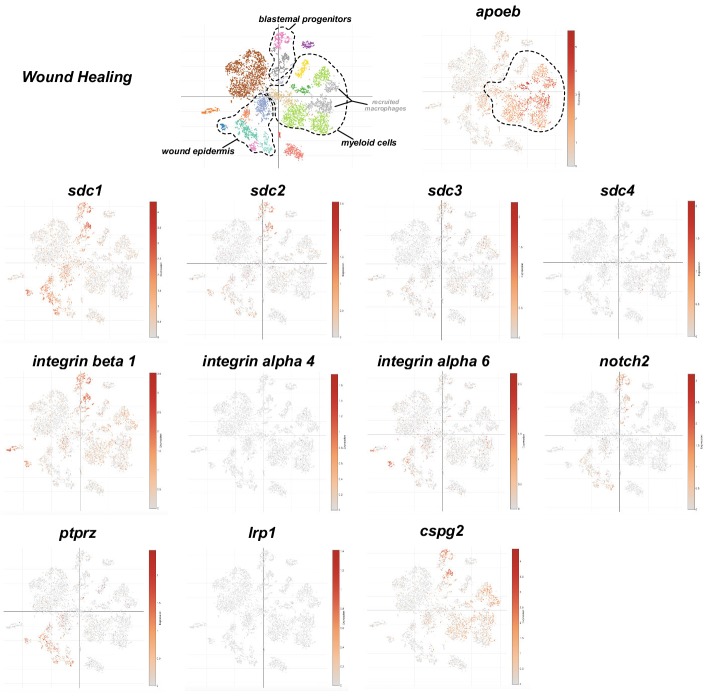
Figure 8. Mk receptors are expressed throughout regenerating tissues.
(A) Heatmap of normalized transcript levels for expressed mk receptors in intact and regenerating subpopulations from our RNA-seq dataset revealed four general patterns of expression (Figure 8—source data 1). (B–C) Double RNAscope in situ hybridization of mk (bright red puncta) with its cognate receptors sdc-1 (B) or ptprz (C) (dark blue puncta). Dotted black line denotes wound epidermis/AEC boundary. Since ptprz expression was low during early stages of regeneration, ptprz/mk in situs were performed without a hematoxylin counterstain to ease visualization of dark blue puncta in the wound epidermis at 7 dpa. Scale bars, B and C (left panel): 25 µm for 63x magnification, C (right panel): 50 µm for 40x magnification. WE, wound epidermis, AEC, apical epithelial cap, bl, blastema, dpa, days post-amputation.